Variational Autoencoders for Generating Synthetic Tractography-Based Bundle Templates in a Low-Data Setting
Highlights
- Convolutional Variational Autoencoder (CVAE) to generate synthetic tractography-based bundle templates from small population data.
Introduction
Tractography-based bundle templates are used to study the brain’s white matter. However, standard white matter atlases are often created from young, healthy adults and may not be representative of other populations such as children or those with neurodegenerative diseases. Prior works using autoencoders to generate synthetic bundles have been limited by the need for large datasets and may be limited by the amount of false-positives in the training data.
Methods
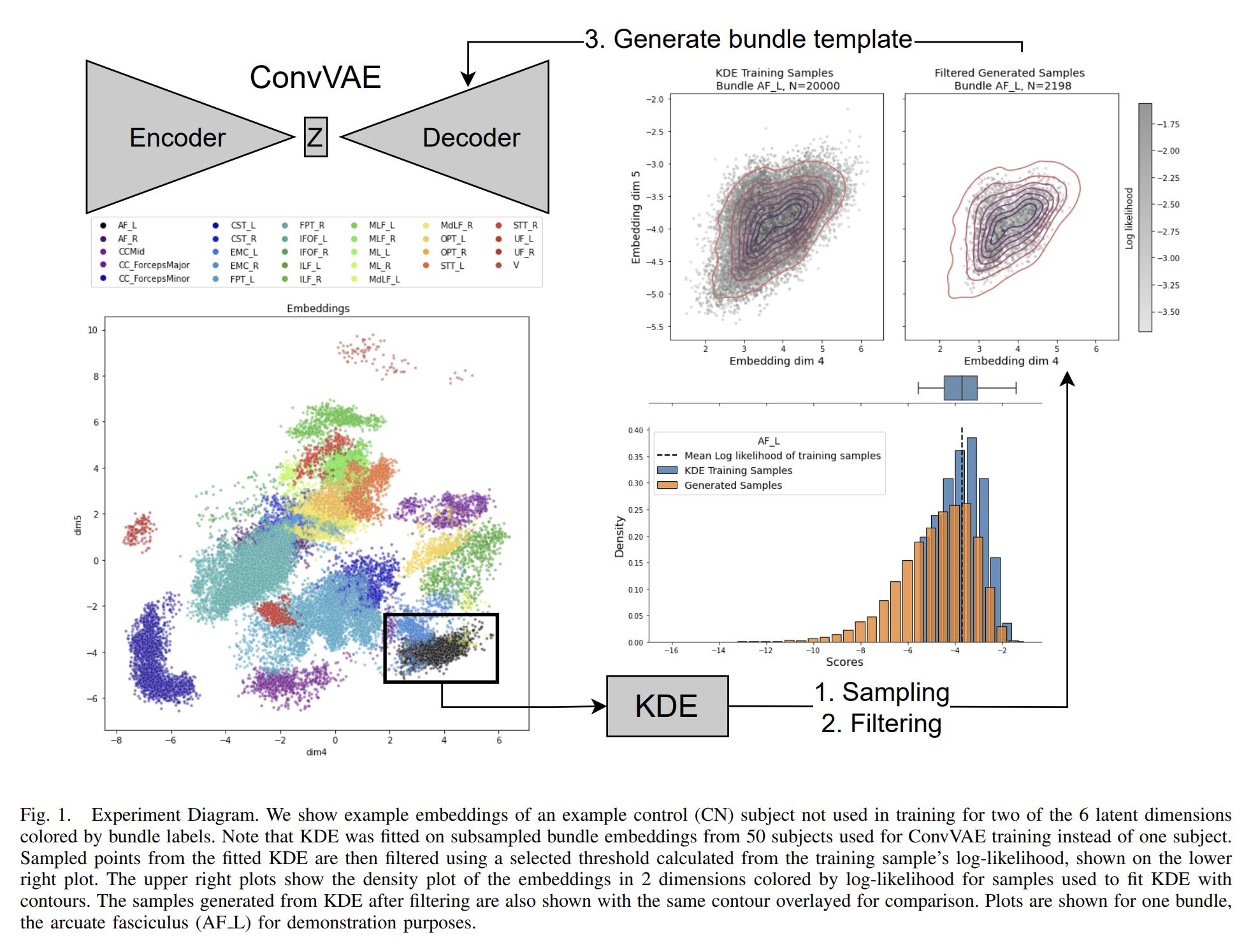
The authors propose a Convolutional Variational Autoencoder (CVAE) to generate synthetic tractography-based bundle templates from small population data. The CVAE is three-layers deep and uses kernels of size 127, 63 and 31 with leaky ReLU, and a small latent space of size 6. “All streamlines from each subject were normalized to fit into a standard sphere, where the centroid and radius are calculated from the atlas data” [sic].
To sample streamlines from the latent space, a Kernel Density Estimator (KDE) is trained per bundle. The KDE is used to filter samples after decoding to remove streamlines below a log-likelihood threshold.
Data
The model is trained on 50 cognitively normal (CN) subjects from the ADNI dataset and tested on 91 CN, mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) subjects from the same dataset.
Results
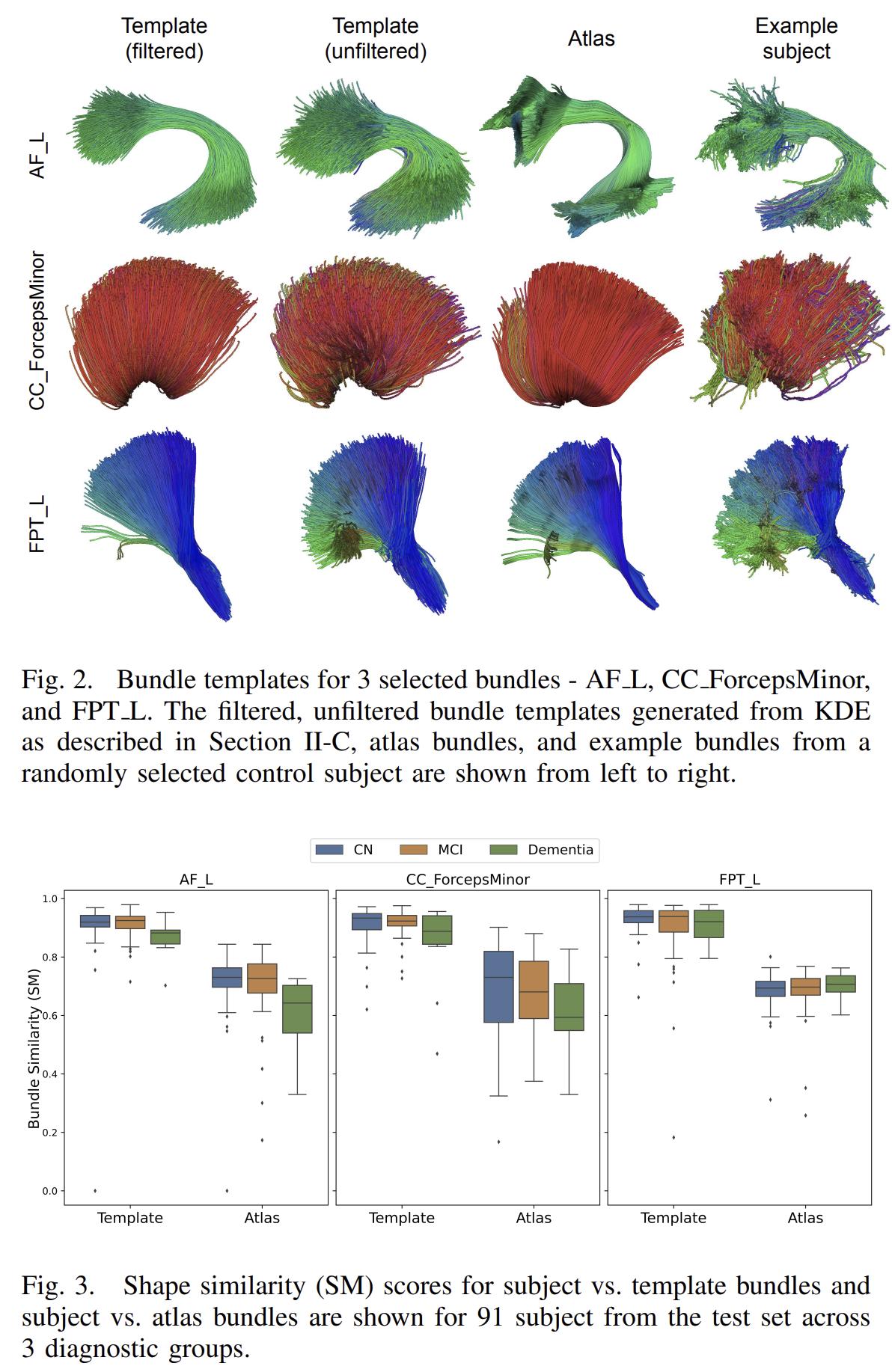
The authors use bundle shape similarity (SM) from the Bundle Analystics (BUAN) framework to compare the decoded bundles to atlas and subject-specific bundles.
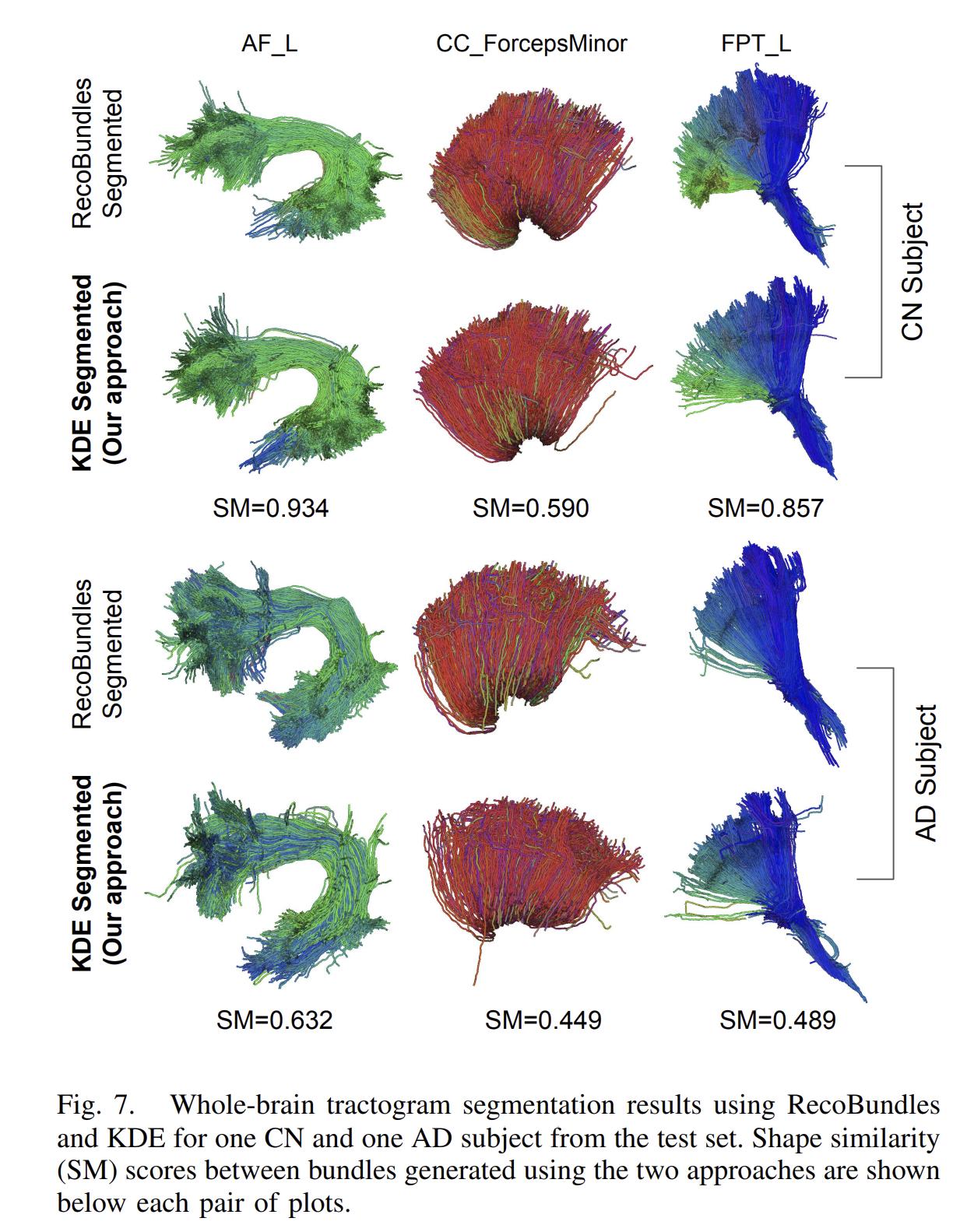
The authors also used the trained KDE to perform whole-brain tractogram segmentation, again using the log-likelihood of the streamlines according to the KDE.
Conclusions
The authors use a CVAE to learn a compact representation of streamlines, and then use KDE to model the distribution of shapes within the learned latent space. This allows for the generation of synthetic bundle templates that capture the shape characteristics of a specific population as well as segmentation of whole-brain tractograms.