Classifyber, a robust streamline-based linear classifier for white matter bundle segmentation
Challenge
- White matter bundle segmentation (volume-based or streamline-based).
- Predict which streamlines/voxels are part of a bundle.
Highlights
Classifyber is a supervised, streamline-based automatic bundle segmentation method that uses a linear classifier. A linear classifier is used because of its interpretability.
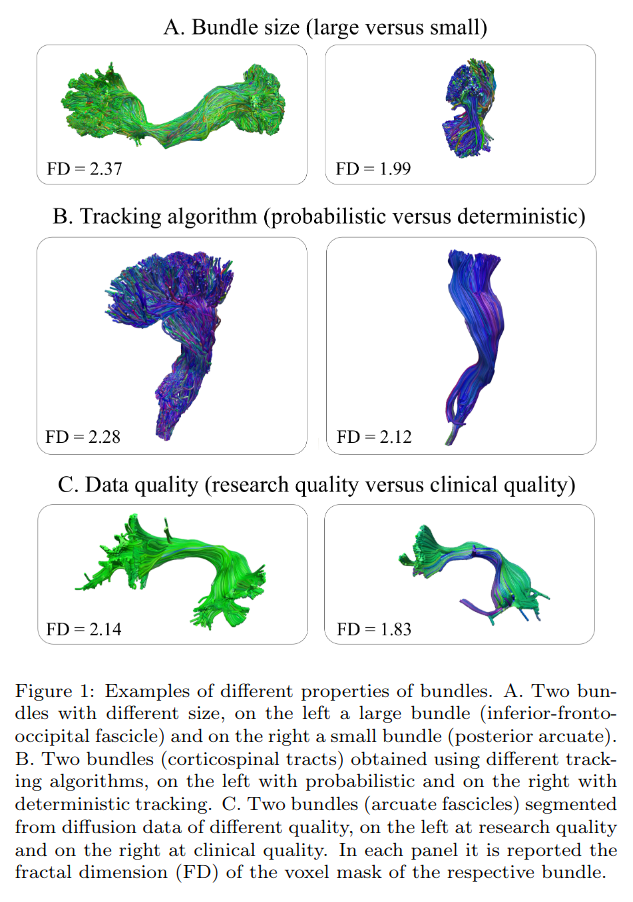
The authors claim that Classifyber is robust to :
- Bundle size (large vs small)
- Tracking algorithm (probabilistic vs deterministic)
- Data quality (research vs clinical)
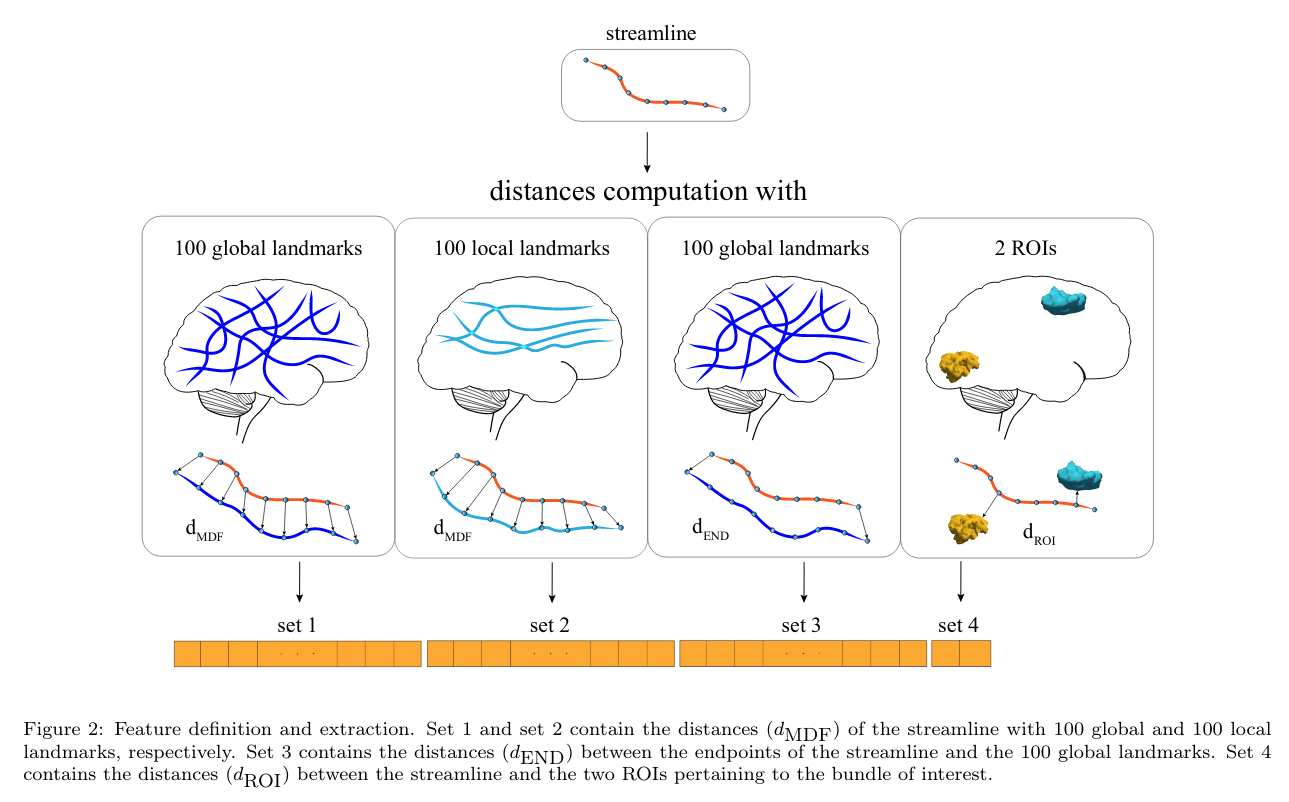
Feature space
The feature space is based on a streamline’s distance to multiple landmarks.
The features are split into 4 sets of local or global features:
- Set 1 (global): MDF distance to 100 streamlines evenly spread over the brain.
- Set 2 (local): MDF distance to 100 streamlines evenly spread over the bundle of interest.
- Set 3 (global): Endpoint distance to 100 streamlines (same as set 1).
- Set 4 (local): Minimum distance to 2 bundle-specific ROIs.
The entire feature space is composed of 302 values. Note that because the feature space is bundle-specific, a different model must be trained for each bundle.
Training procedure
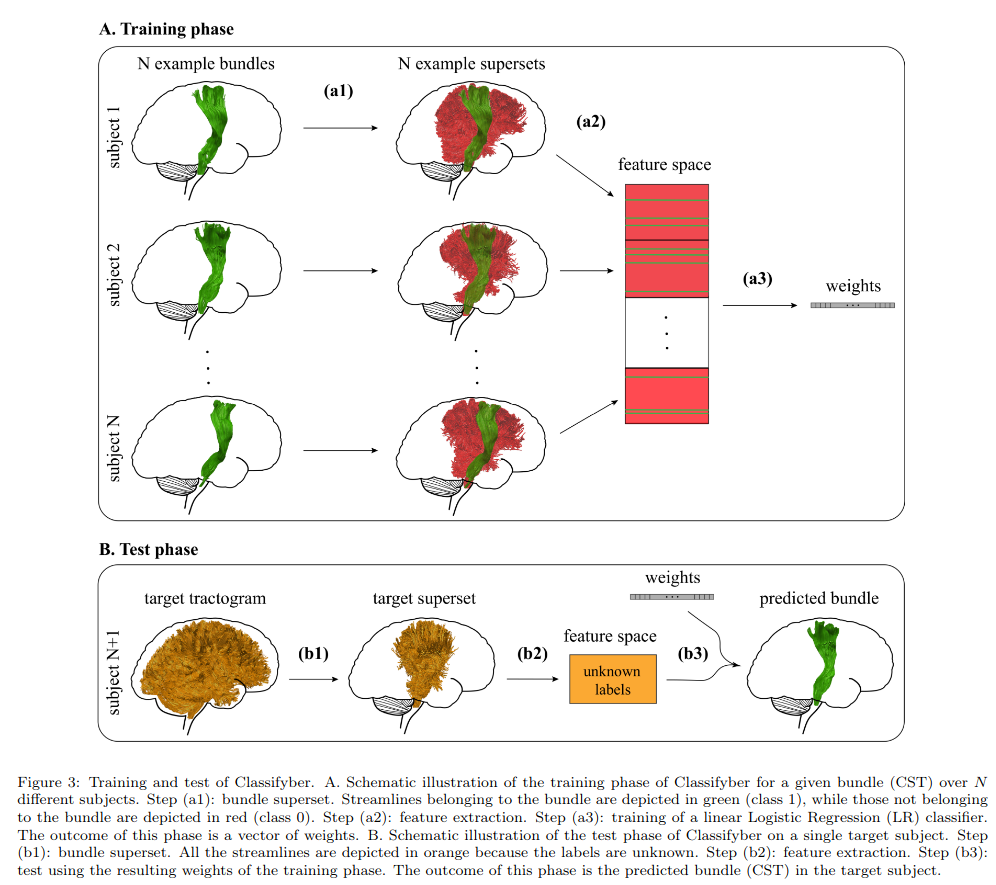
(a1) Bundle superset: Build bundle dataset from the positive examples and their (negative) neighbors.
(a2) Feature extraction: Each streamline is converted to a feature vector of 302 values and assigned a 0-1 label.
(a3) Training: Train a binary Logistic Regression classifier (using a fast stochastic average gradient descent solver) to get a vector of weights (of 302 values).
(b) Testing procedure: The whole tractogram is reduced to a bundle superset corresponding to the target bundle, estimated from training samples. The trained weights are used to predict the class label of each streamline.
Data
Combinations of manual and automatic segmentations:
- HCP-minor: 105 subjects, 8 bundles, semi-automatic segmentation
- HCP-major: 105 subjects, 10 bundles, semi-automatic segmentation (TractSeg)
- HCP-IFOF: 30 subjects, 2 bundles, expert segmentation
- Clinical: 10 subjects with brain tumor, 2 bundles, expert segmentation
Baselines
- TractSeg (ML volume segmentation)
- RecoBundles (Similarity score based on pre-defined bundle models)
- LAP (Linear Assignment Problem; seems to be a k-NN approach)
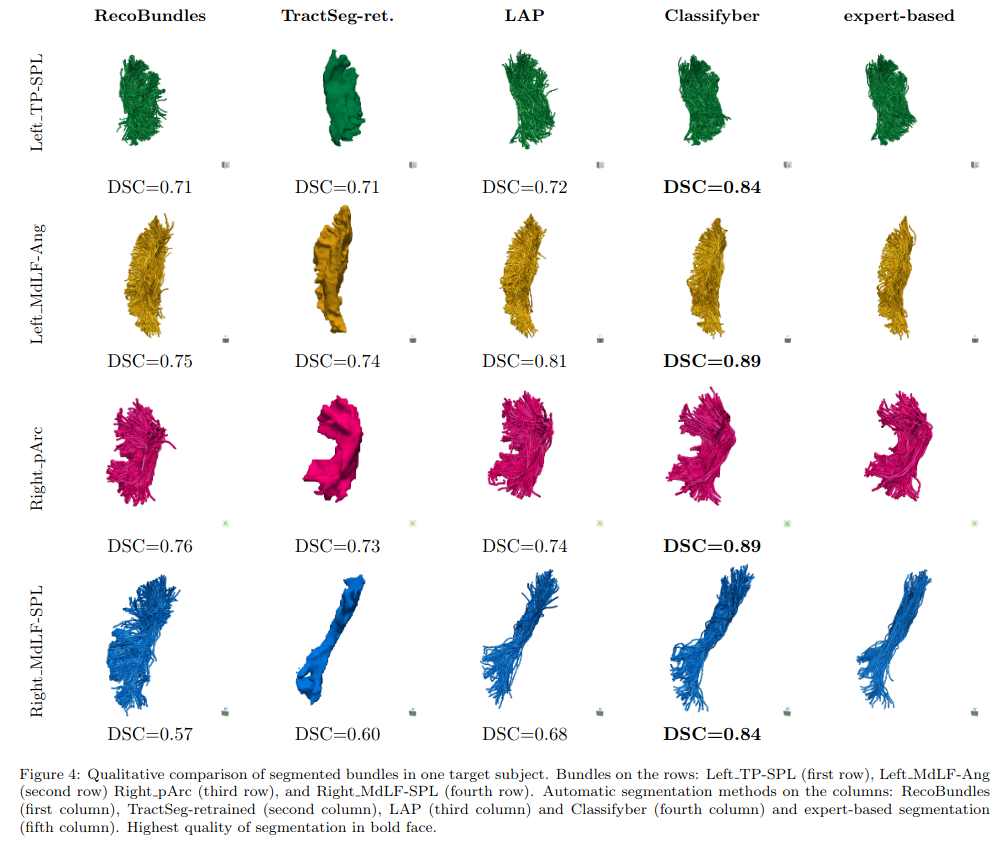
Experiments
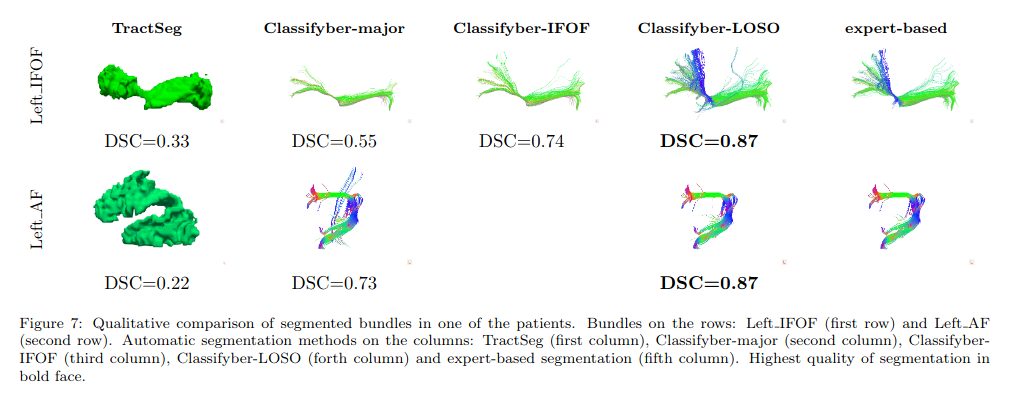
Notes
- Classifyber requires all subjects to be registered in the same space to compute its feature vector.
- Classifyber is retrained for each bundle and each dataset. This is possible because it is fast to train, but may indicate a lack of generalizability.
- Test phase (b2): The authors reduce the whole-brain tractogram to a bundle superset estimated using training examples. This may bias their results towards a positive score by removing possible false positives from the whole-brain tractogram.
- TractSeg and RecoBundles were retrained only when the bundle of interest was not available in the base model, whereas Classifyber was trained specifically on all the expert segmentations. This may also be an unfair advantage because of the different train sets.