Manifold mixup: Encouraging meaningful on-manifold interpolation as a regularizer
Highlights
- Simple regularization method that encourages neural networks to predict less confidently on interpolations of hidden representations
- Smoother decision boundaries
- Learned representations with less directions of variance
- Better generalization than other competitive regularizers (e.g. dropout)
- Improved robustness to adversarial attacks
Method
Manifold mixup is based on Input Mixup, where pairs of inputs and targets are interpolated to create new data.
“[…], mixup regularizes the neural network to favor simple linear behavior in-between training examples.”
Manifold mixup is a simple data augmentation method, which consists of interpolating pairs of hidden activations of inputs and labels (one-hot encodings for classification)
Procedure:
- Select a random layer in the network (may include the input layer)
- Sample two minibatches of data, and run them through the network up to the selected layer
- Perform Input mixup by sampling pairs of inputs/labels, and interpolating between them to build a “mixed minibatch”
- Run the mixed minibatch through the rest of the network to produce the output
- Compute the loss between the output and the “mixed label” (interpolation between the original labels)
-
Smoother decision boundaries
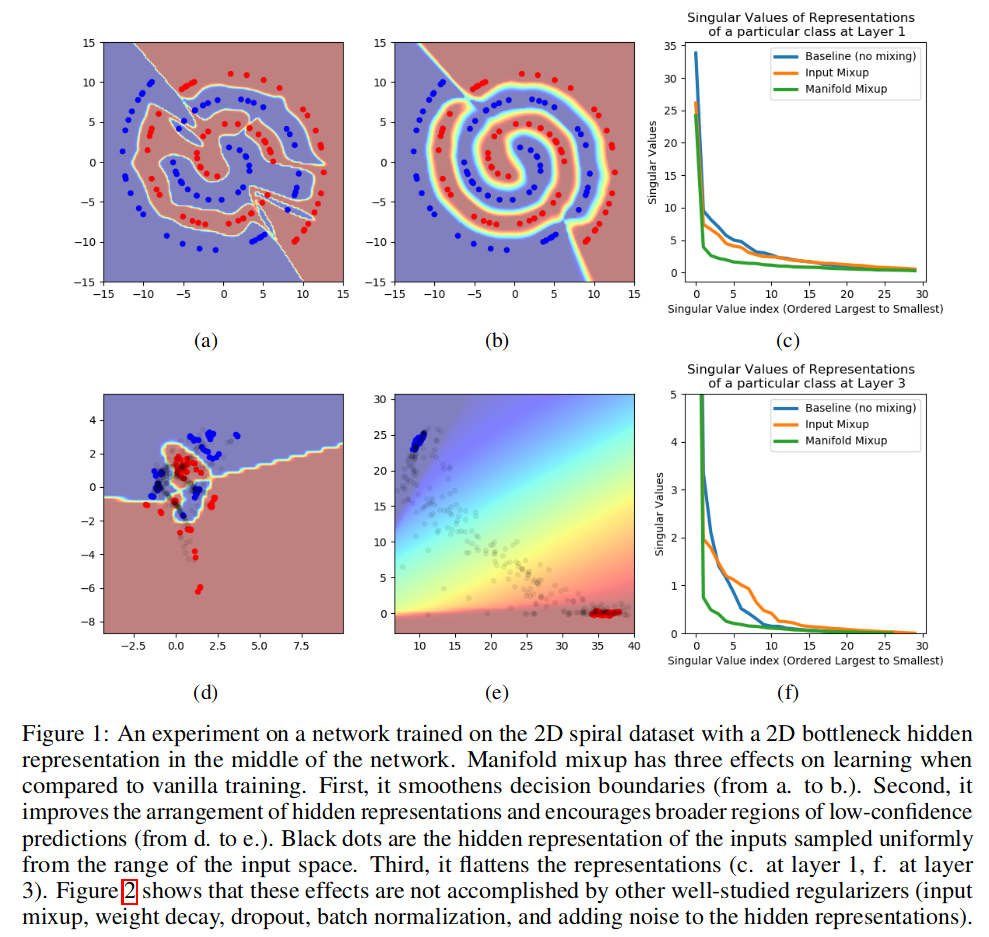
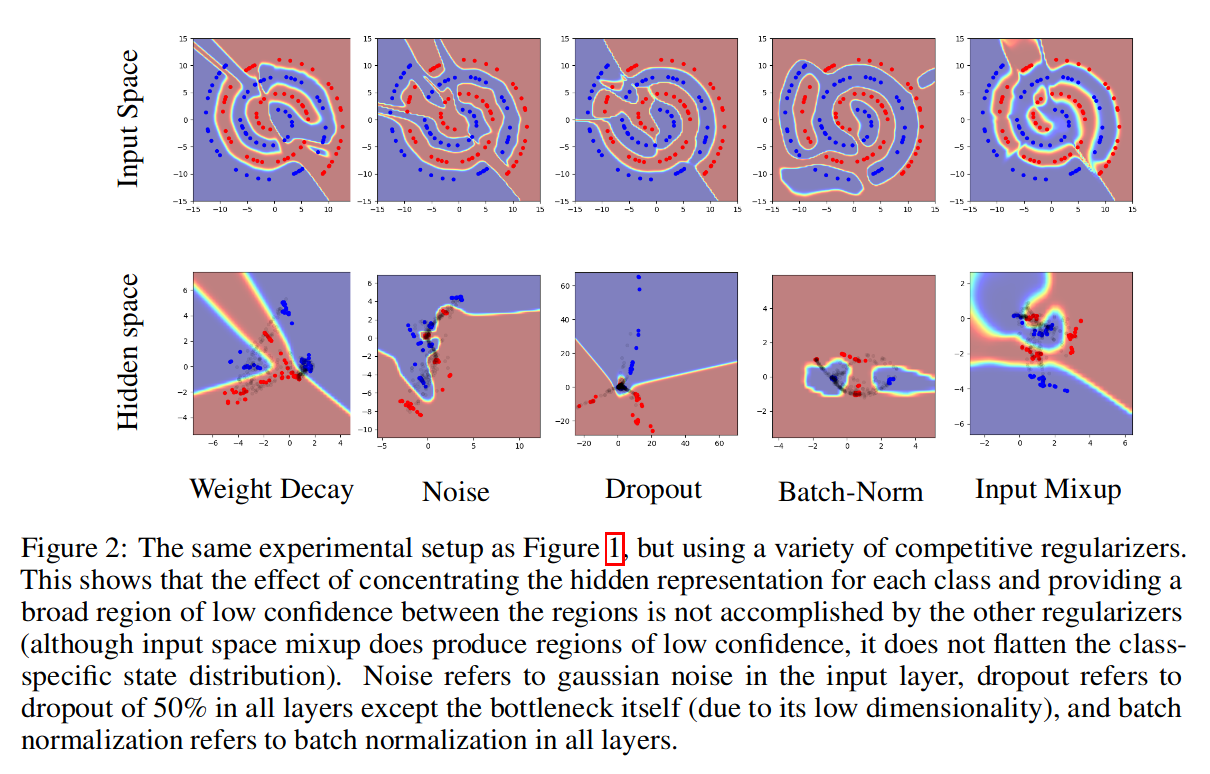
-
Concentration of hidden states with regions of low confidence
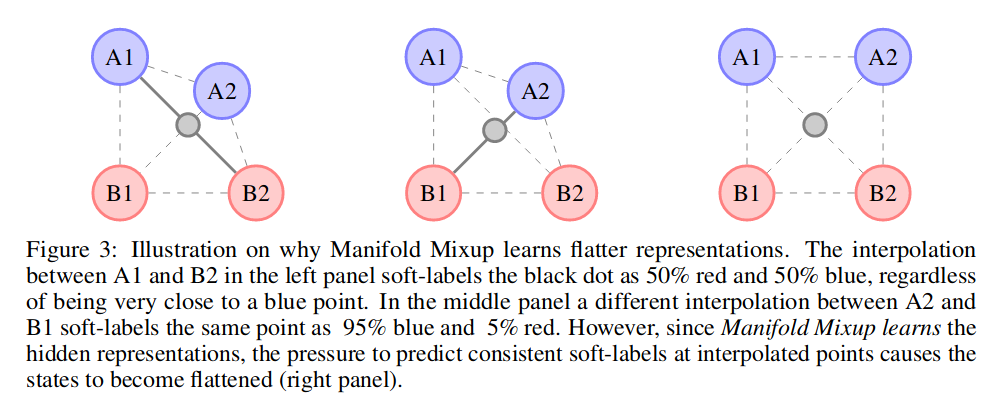
-
Flattening effect on the hidden states
Experiments
Results
-
CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100
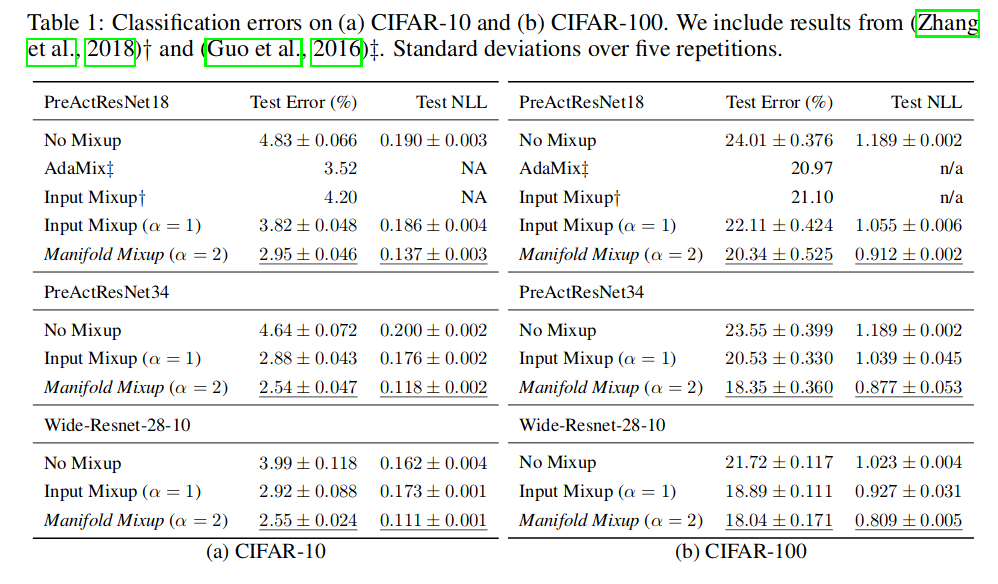
-
SVHN
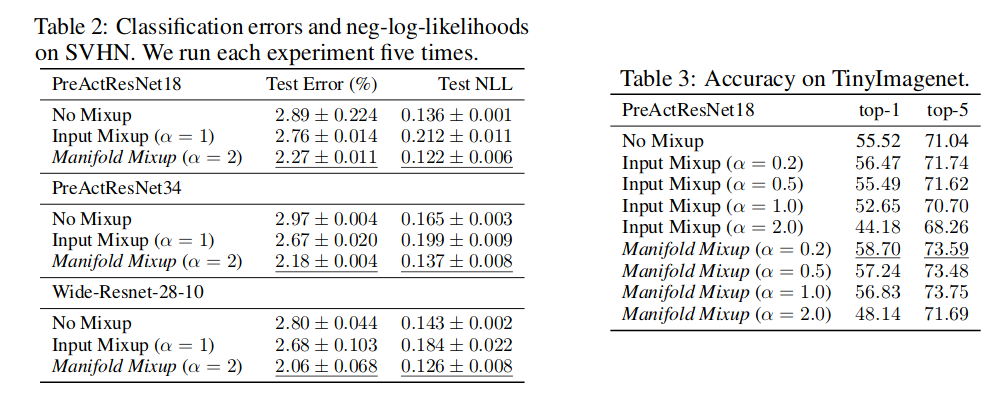
-
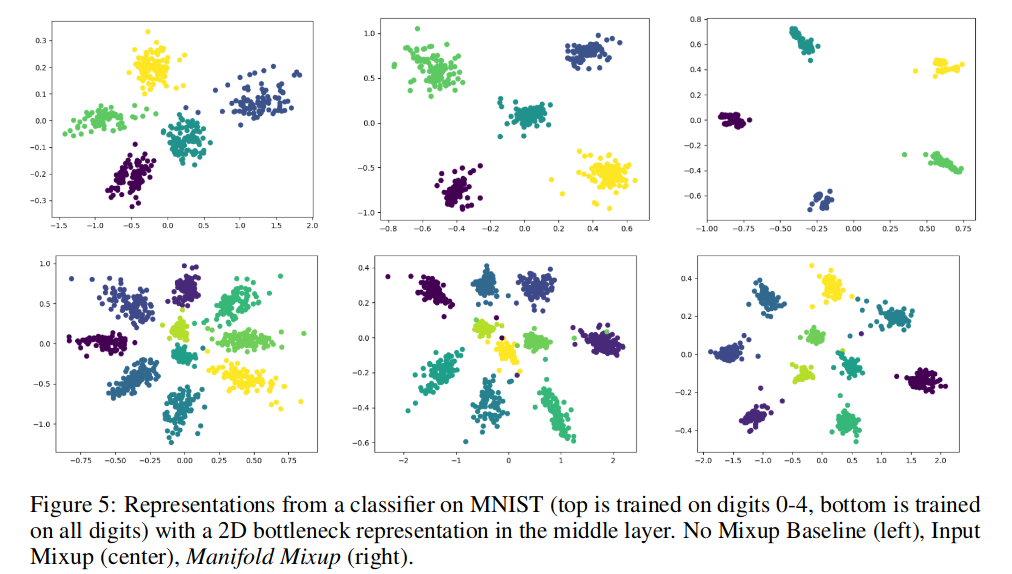
MNIST learned representations