Learning how to Active Learn: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach
Summary
Here the authors present an RL method applied to active learning. As mentioned in the abstract :
Active learning aims to select a small subset of data for annotation such that a classifier learned on the data is highly accurate. This is usually done using heuristic selection methods, however the effectiveness of such methods is limited and moreover, the performance of heuristics varies between datasets. To address these shortcomings, we introduce a novel formulation by reframing the active learning as a reinforcement learning problem and explicitly learning a data selection policy, where the policy takes the role of the active learning heuristic.
Proposed method
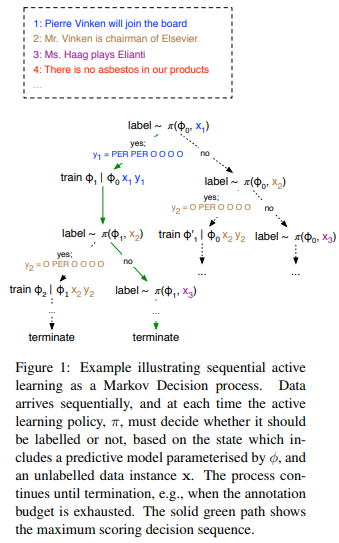
On one side, there is a labeling network with parameters \(\phi\) that is trained on a dataset D to label text. On the other side, there is a policy network \(\pi\) that predicts if a sentence \(x_i\) should be labeled by an oracle or not. If yes, then the sequence is labeled, added to the training dataset D and the labeling network is retrained. The reward is given by
\[R(s_{i−1}, a) = Acc(\phi_i) − Acc(\phi_{i-1})\]where \(s_i\) is the state and \(a\) is an action (label or do not label). The state is given by the concatenation of an embedding of each word of the sentence \(x_i = {x_{i,1}, x_{i,2}, ... , x_{i,n}\) as well as the output \(p_\phi(x_i)\) of the labeling network.
The method is illustrated in Fig.1 and described in more details in Algo 2.

Results
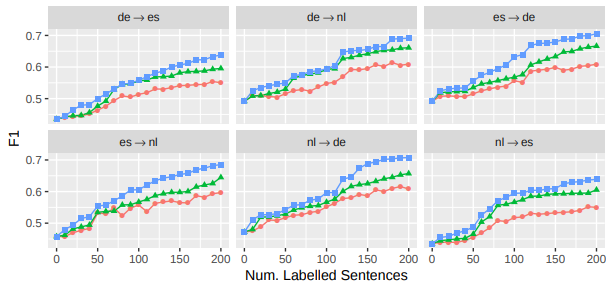
Results on translation tasks are quite convincing.