Fully Convolutional Network with Multi-Step Reinforcement Learning for Image Processing
Introduction
Reinforcement learning methods are typically used to control robots and have only recently been used for image processing purposes. The authors of the paper do the latter by assigning an agent per pixel, where the agent changes the pixel value by taking an action. They apply the method to three image processing tasks: Image denoising, image restoration and local color enhancement. They claim to achieve comparable or better performances than state-of-the-art methods, as well as having more interpretability than supervised methods.
Method
They extend A3C by assigning an agent to each pixel of the image, where each agent trains a Policy Network to determine the best action to take and a Value Network that tries to approximate the future rewards. Of course, it would be computationally impractical to have a single network per agent, therefore the authors used a Fully-Convolutional Network to have the agents share the same network.
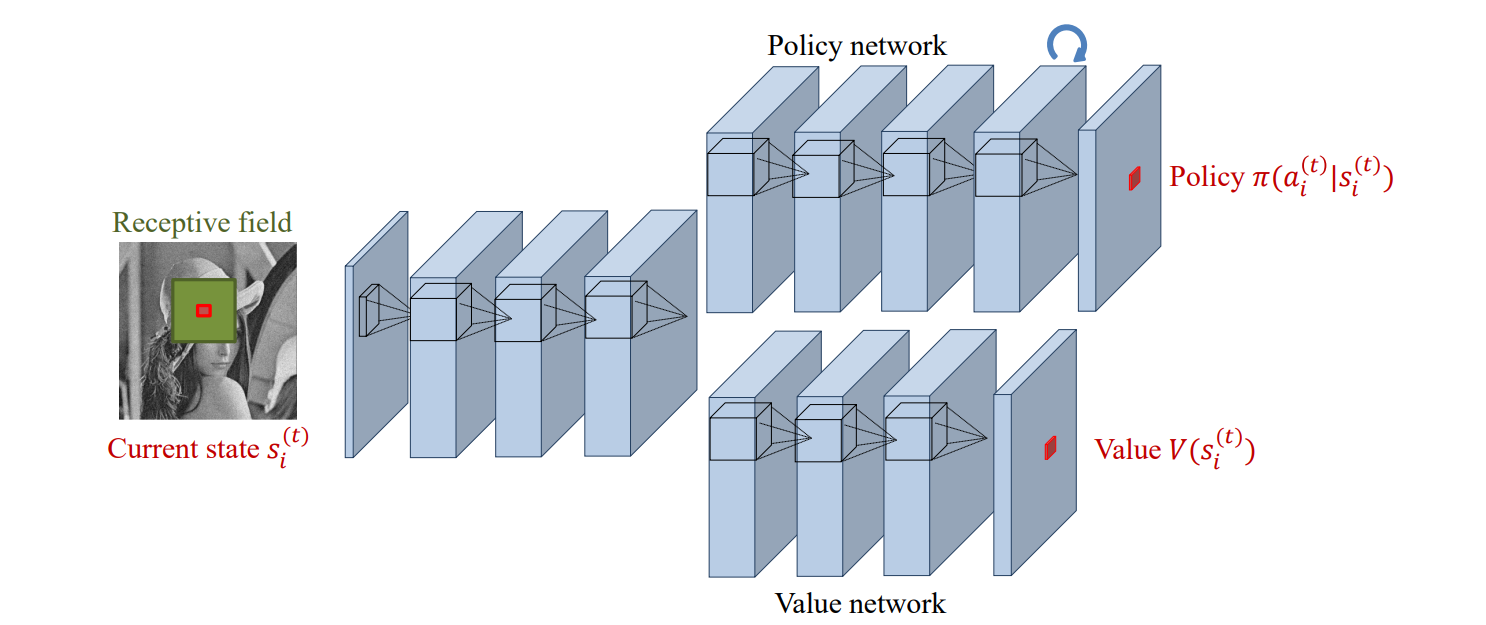
All the components are trained as they normally would
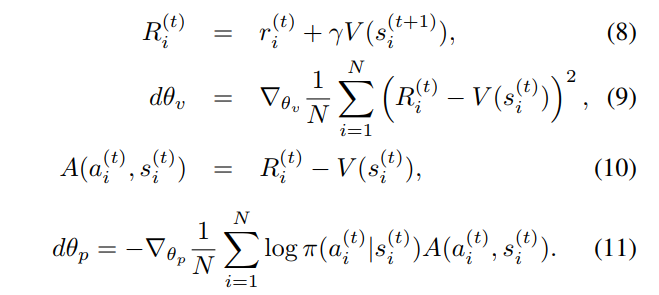
However, you can usually boost the performance of a CNN by enlarging its receptive field. The authors therefore defined the Reward Map Convolution as
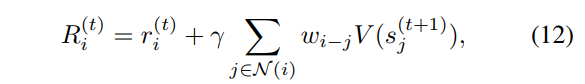
where \(w_i-j\) is the weight of how much we consider the values \(V\) of the neighbor pixels at the next time step, and \(w\) can be regarded as a convolution filter weight that is trained alongside \(\theta_p\) and \(\theta_v\).
The reward is defined as
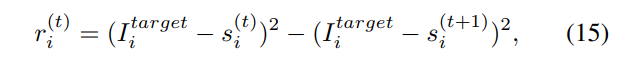
Results
Image denoising
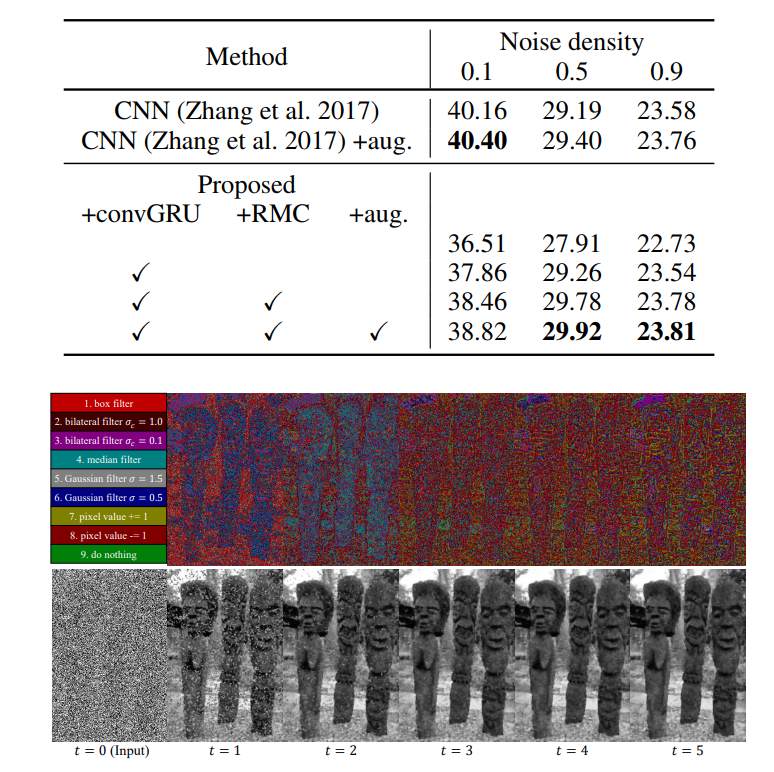
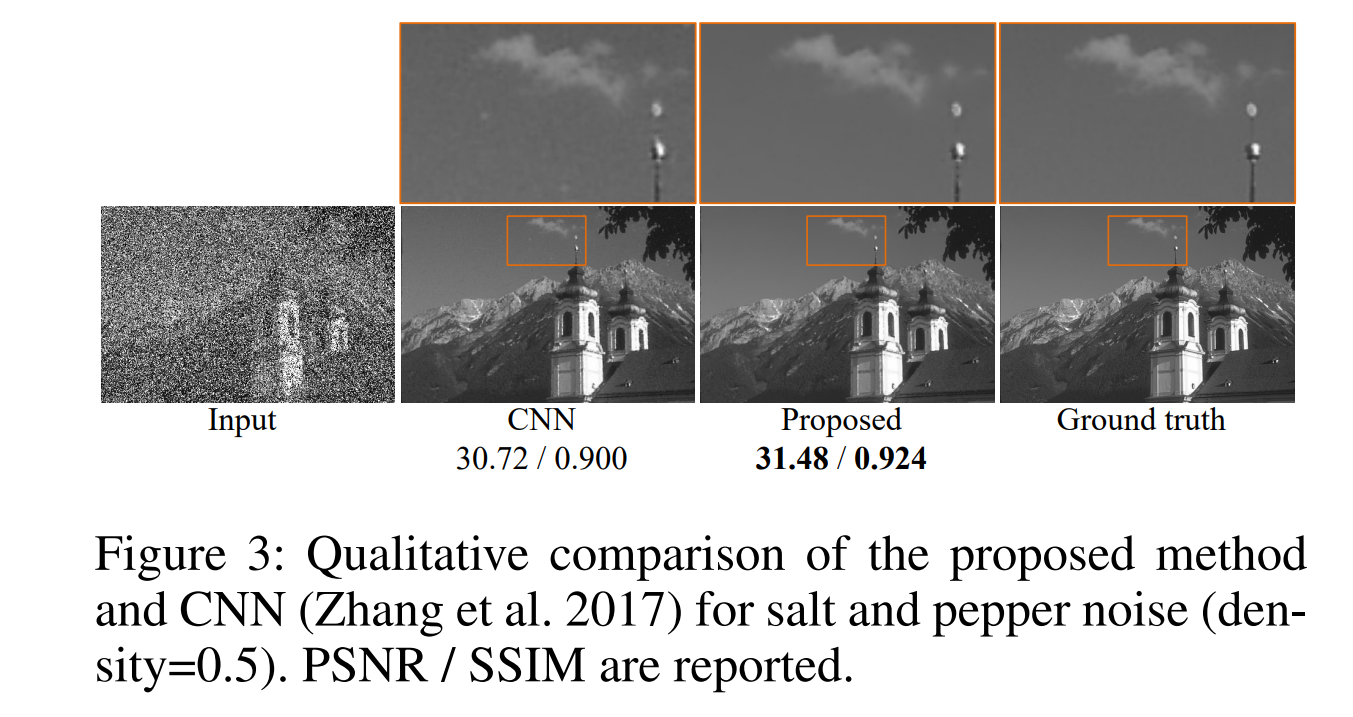
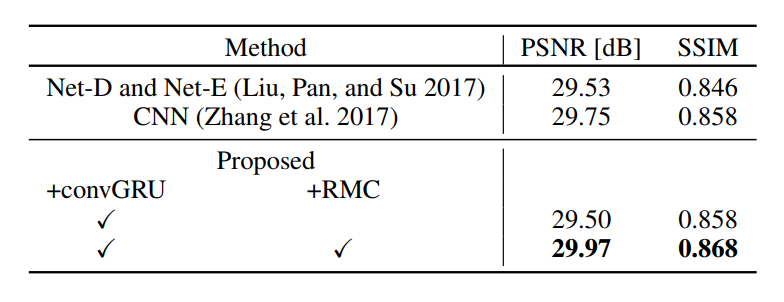
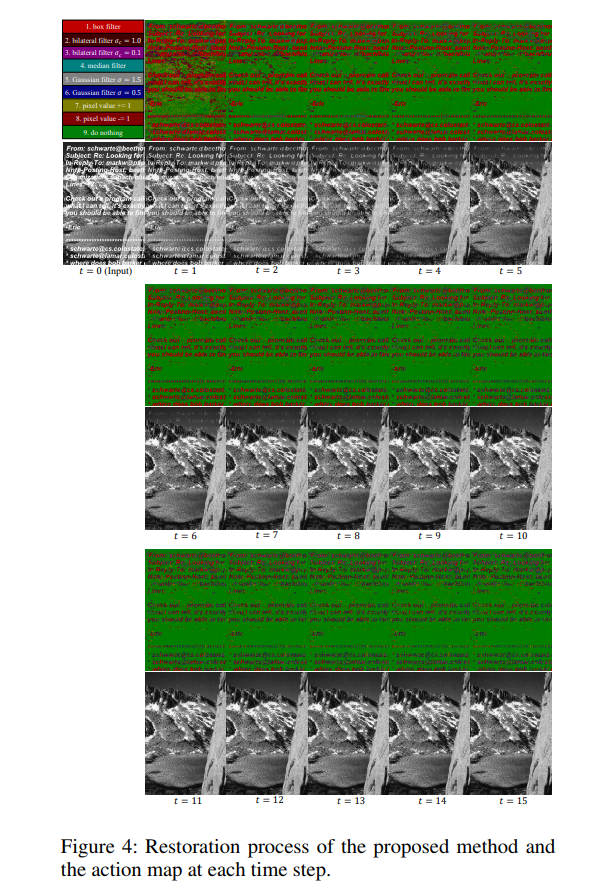
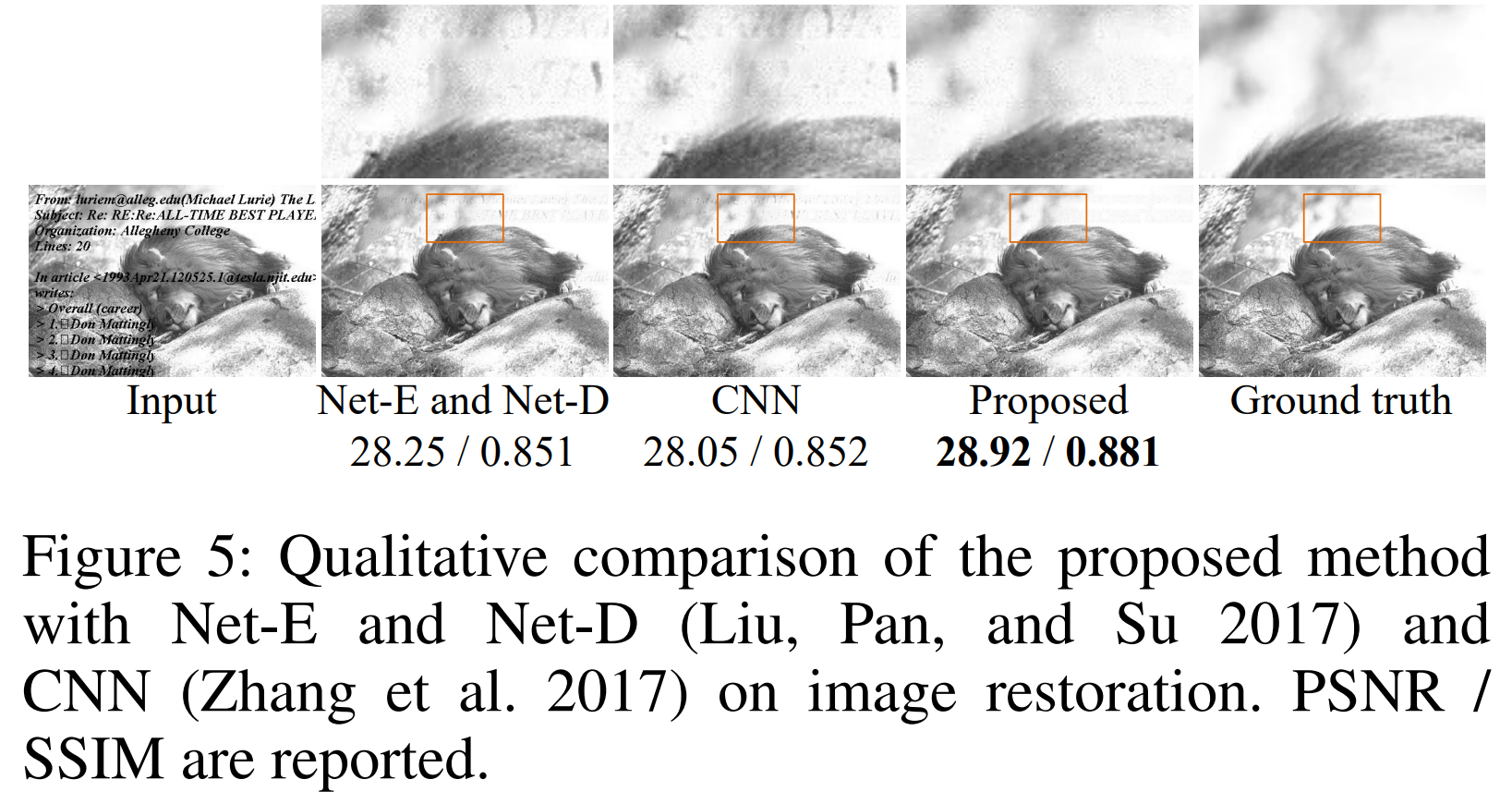
Image resoration
 —
—
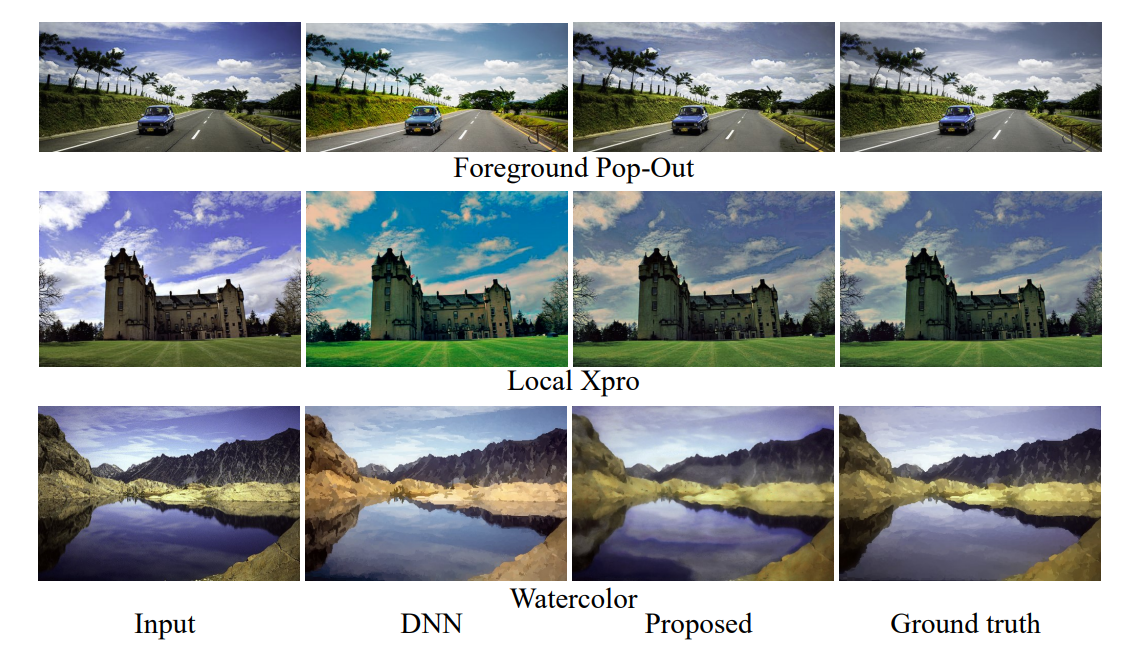
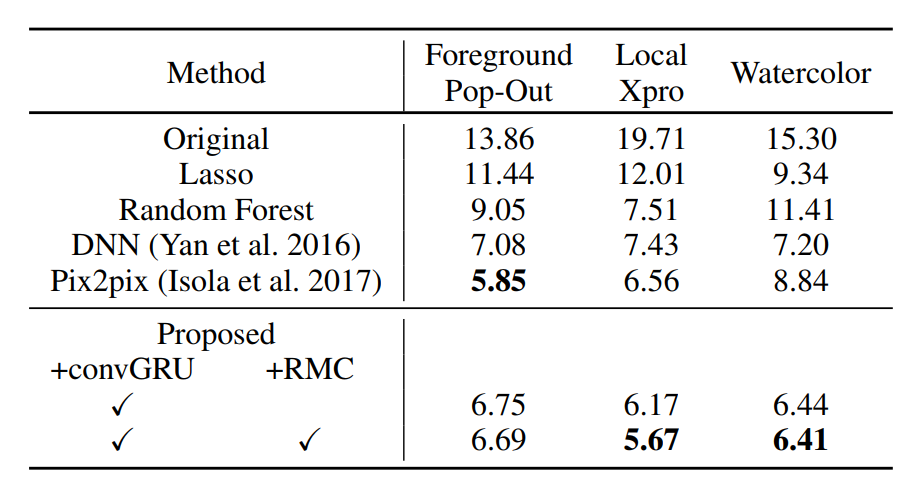
Color enhancement