Adaptive Fusion for RGB-D Salient Object Detection
Code: https://github.com/Lucia-Ningning/Adaptive_Fusion_RGBD_Saliency_Detection
Summary
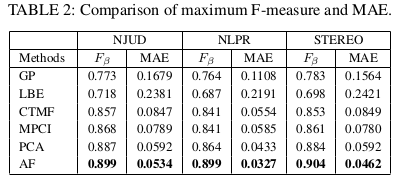
The RGB-D images are used in salient object detection to identify the most visually distinctive objects in a pair of color and depth images.
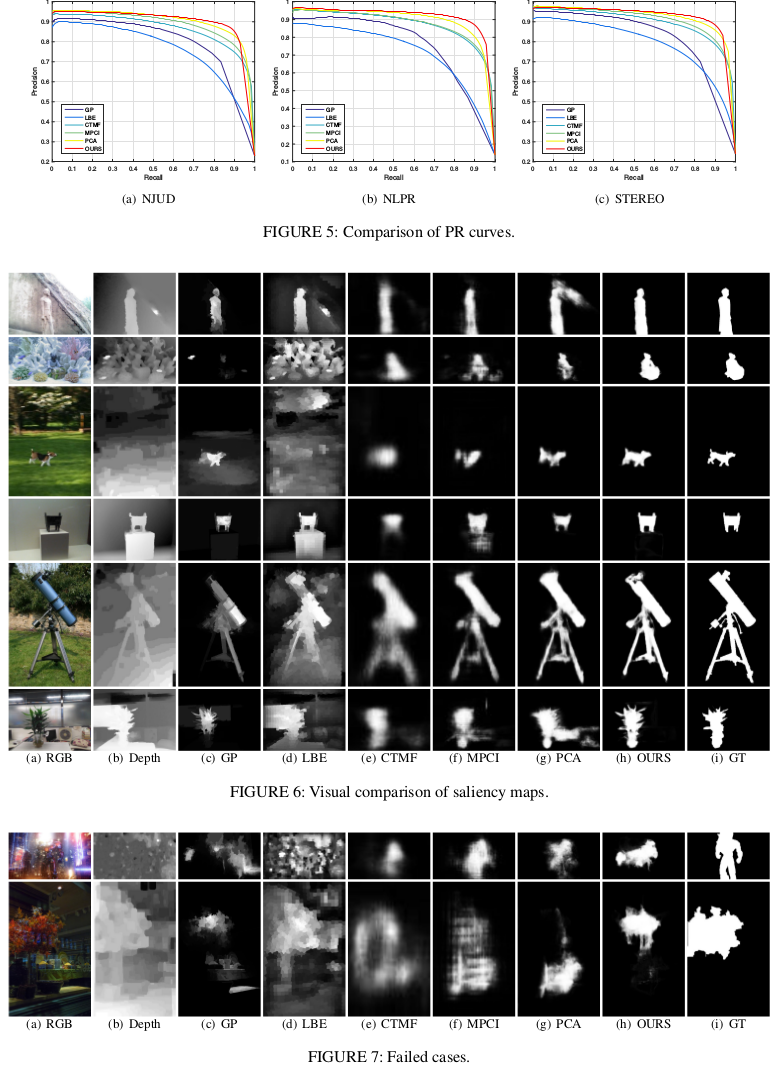
They design a two-streamed convolutional neural network (CNN), each of which extracts features and predicts a saliency map from either RGB or depth modality.
To have full supervision of the network, they added three losses: saliency supervision, switch map supervision, and edge-preserving constraints.
Method
They say they have two significant concerns existing in RGB-D saliency detection for achieving better performance: how to model the depth-induced saliency, and how to fuse RGB and depth modalities.
Saliency Fusion Module
The switch map is a 1-channel image whose pixel values are assigned in [0, 1]. This will play a role to adaptively weigh the RGB and depth predictions, and therefore the fused saliency map is a weighted sum of the two predictions.
\[Y^{sw}=S^{rgb} \odot Y +(1-S^{rgb})\odot (1-Y)\] \[S^{fused}=SW \odot S^{rgb}+(1+SW) \odot S^{d}\]Loss Function
Saliency Loss. There are three saliency maps produced in the network, they applied a standard cross-entropy for each. \(L_{sal}=L^{rgb}_{sal}+L^{d}_{sal}+L^{fused}_{sal}\).
\[L^{m}_{sal}=-\sum^{N}_{i=1}\sum^{T}_{j=1}(y_{i,j}\log S^{m}_{i,j}+(1-y_{i,j})\log (1-S^{m}_{i,j}))\]Switch Loss. They use another cross-entropy with the switch map generated.
\[L_{sw}=-\sum^{N}_{i=1}\sum^{T}_{j=1}(y^{sw}_{i,j}\log SW_{i,j}+(1-y^{sw}_{i,j})\log (1-SW_{i,j}))\]Edge-preserving Loss. The edge-preserving property has been considered previously RGB saliency detection works to obtain sharp salient object boundaries and improve detection performance.
\[L_{edge}=\frac{1}{N}\sum^{N}_{i=1}\| \partial_{x}(S^{fused}_{i})-\partial_{x}(Y_{i})\|^{2}_{2}+\| \partial_{y}(S^{fused}_{i})-\partial_{y}(Y_{i})\|^{2}_{2}\]Where \(\partial_{x}\) and \(\partial_{y}\) are gradients in horizontal and vertical direction respectively.
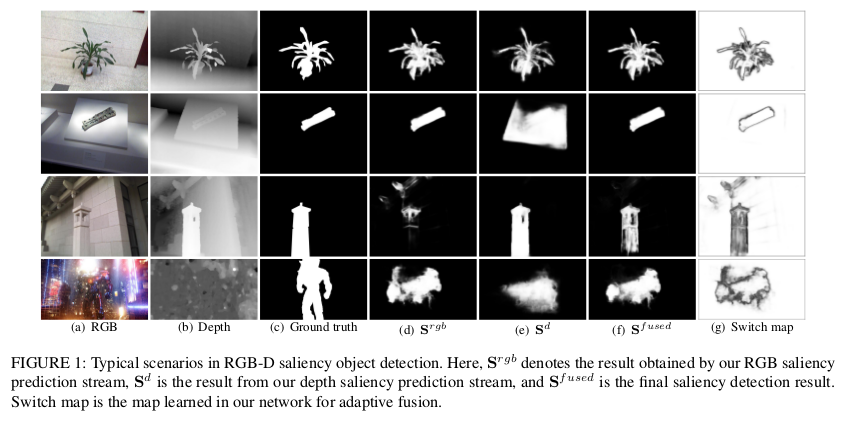
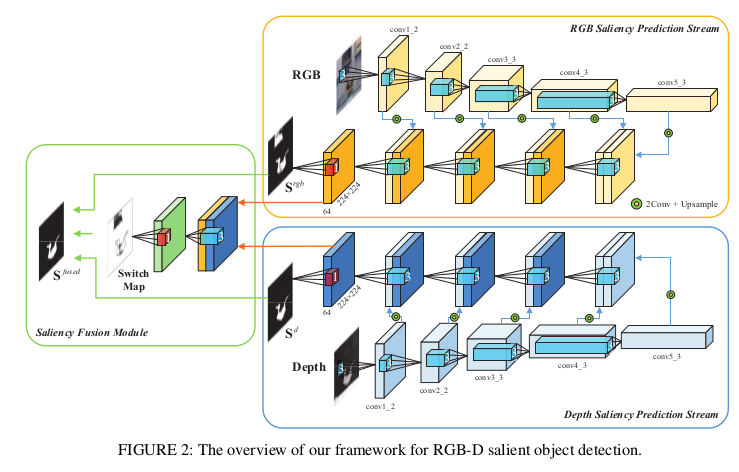
Results