Suggestive Annotation: A Deep Active Learning Framework for Biomedical Image Segmentation
Description
The authors address the following question: With limited effort (e.g., time) for annotation, what instances should be annotated in order to attain the best performance? For this, they present a deep active learning framework that combines fully convolutional network (FCN) and active learning to reduce annotation effort. The method is summarized in Figure 1.
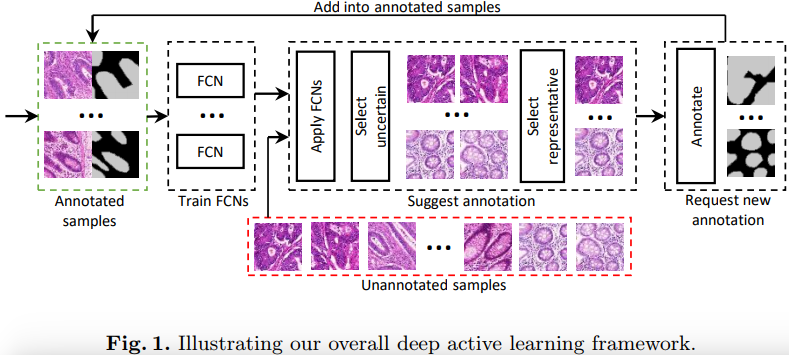
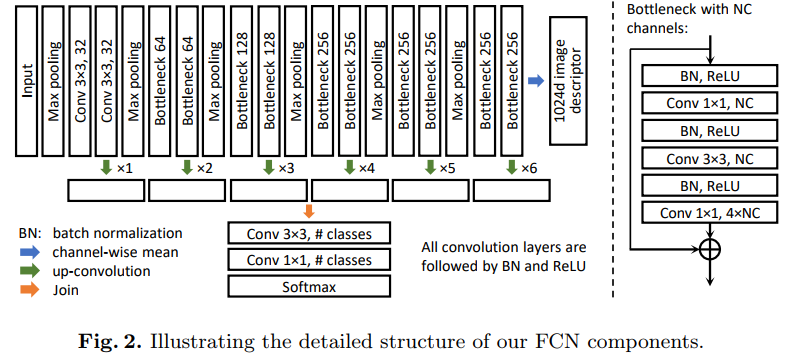
The method
The method works as follows:
- Start with a small training set
- Train a series of FCN segmentation networks such as the on in figure 2.
- Segment a set of unannotated images with all the FCNs
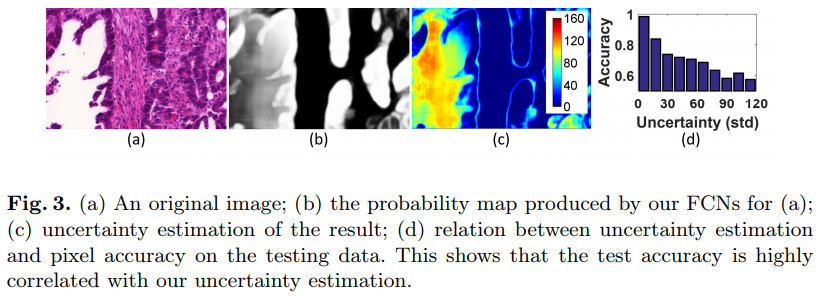
- For each unannotated image, measure at each pixel how much the FCNs disagree. This provides an uncertainty measure as in figure 3.
- Select the N unannotated images with the largest amount of uncertainty
- From those N images, select the M<N most “representative”.
- Ask someone to manually annotate the M images and put those newly annoted images in the training set
- GOTO 2 until uptimal accuracy reached.
NOTE: an image is representative when its 1024 descriptor is close to that of many other unannotated images.
Results
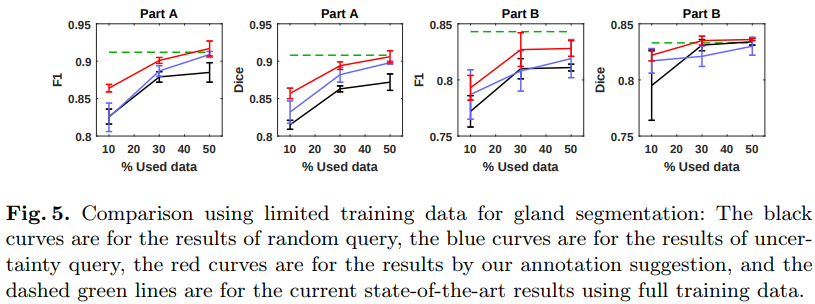
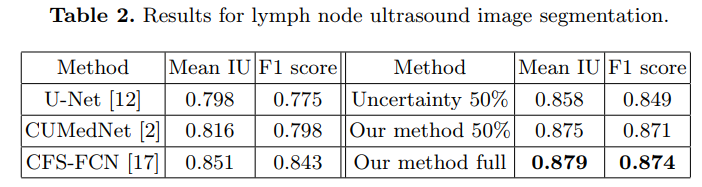
Their method is better than random selection (c.f. figure 5) and beat other state-of-the-art methods (c.f. Table 2)