Automatic 3D bi-ventricular segmentation of cardiac images by a shape-constrained multi-task deep learning approach
Introduction
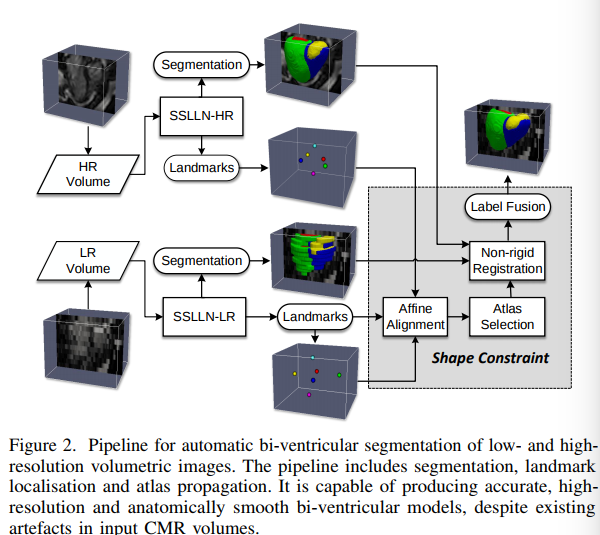
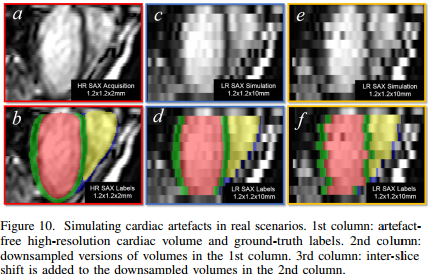
This paper proposes a method for MRI cardiac segmentation built upon a shape prior. The method seems to work well both on high and low resolution images (i.e. 3D images with small and large inter-slice thickness). The overall method is illustrated in Figure 2. In short, the method first segments the input image and locates 6 anatomical points as shown in figure 3. Note that the full 3D volume is fed to the Network but only conv2D operations are used in the rest of the network. Then, the anatomical points are used to register the 3D shape prior which is then combined to the segmented result.
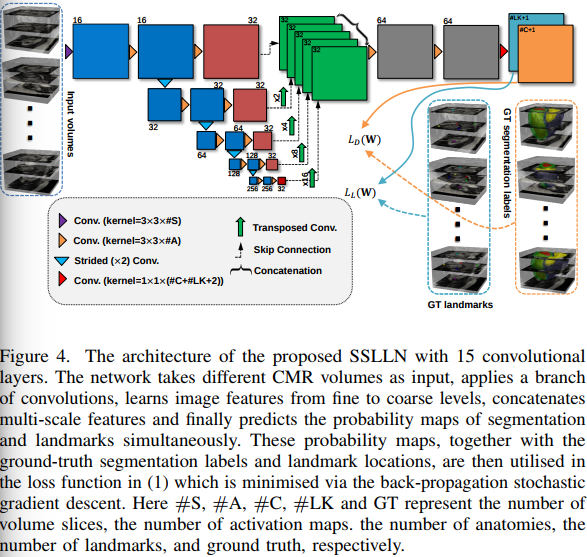
Further details.
The loss involves 3 terms:
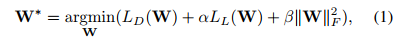
where \(L_D(W)\) is the segmentation loss that evaluates spatial overlap with ground-truth labels and \(L_L(W)\) is the landmark associated loss for predicting landmark locations.
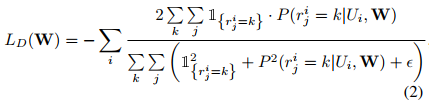
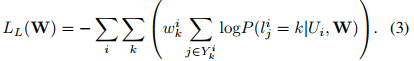
Results
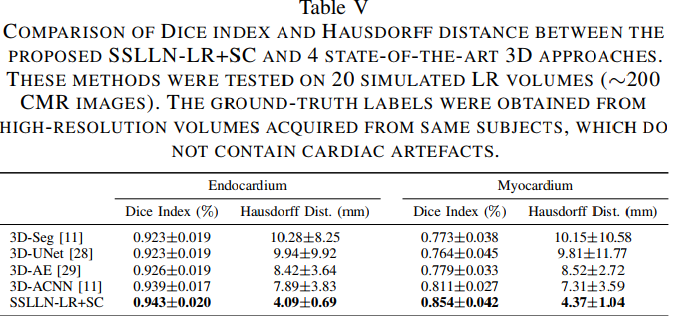
Results are convincing both on high and low resolution images. The method also seems to out perform state-of-the-art methods.