Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation
Main Idea
They propose a Dual Attention Networks (DANet) to adaptively integrate local features with their global dependencies, unlike previous works that capture contexts by multi-scale feature fusion. Specifically, they append two types of attention modules on top of traditional dilated FCN. The position attention module selectively aggregates the features at each position by a weighted sum of the features at all positions. Attention module selectively emphasizes interdependent channel maps by integrating associated features among all channel maps.
Dual Attention Network
The model is filled with pictures of scene segmentation with diverse scales, lighting, and views.
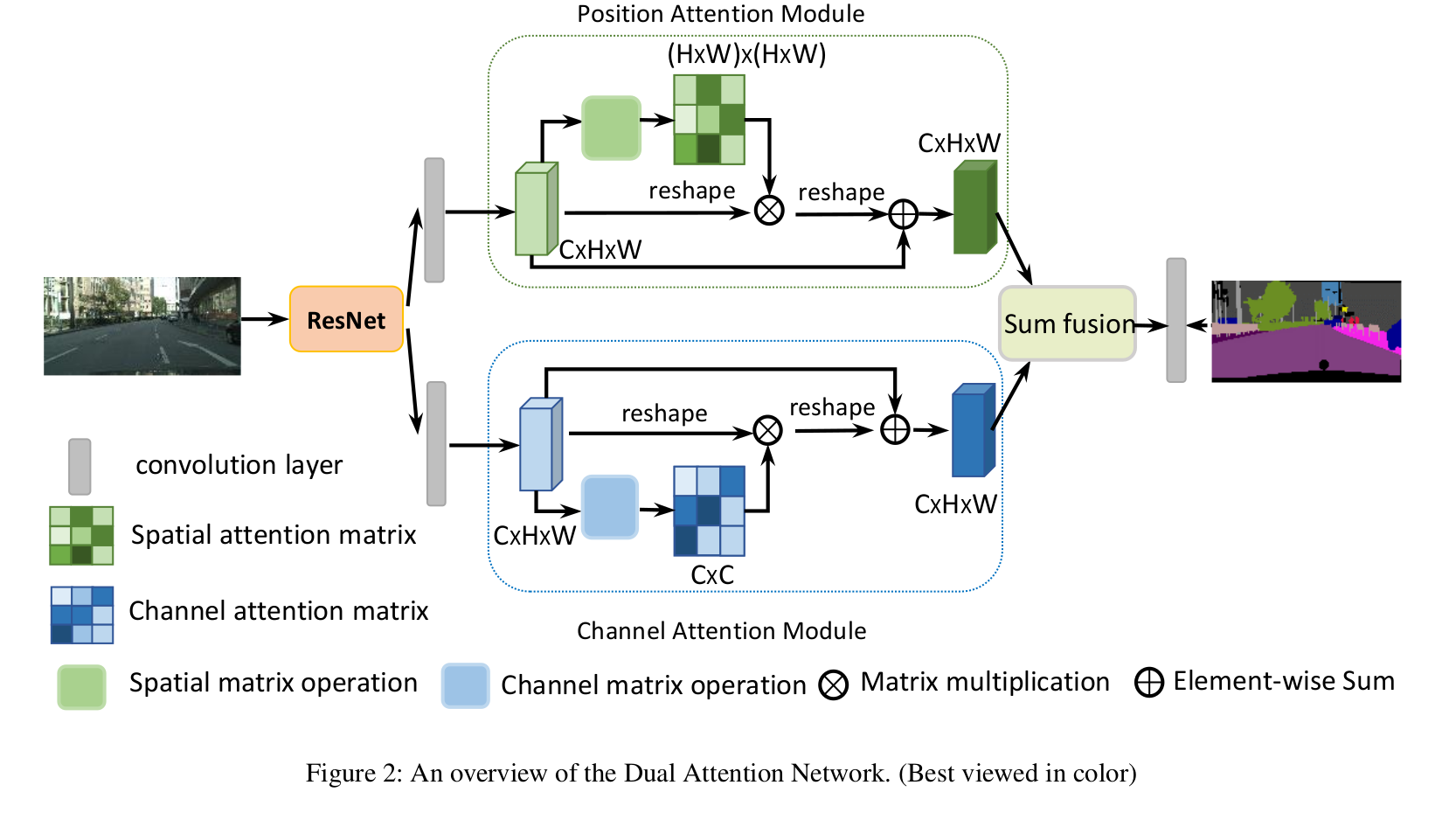
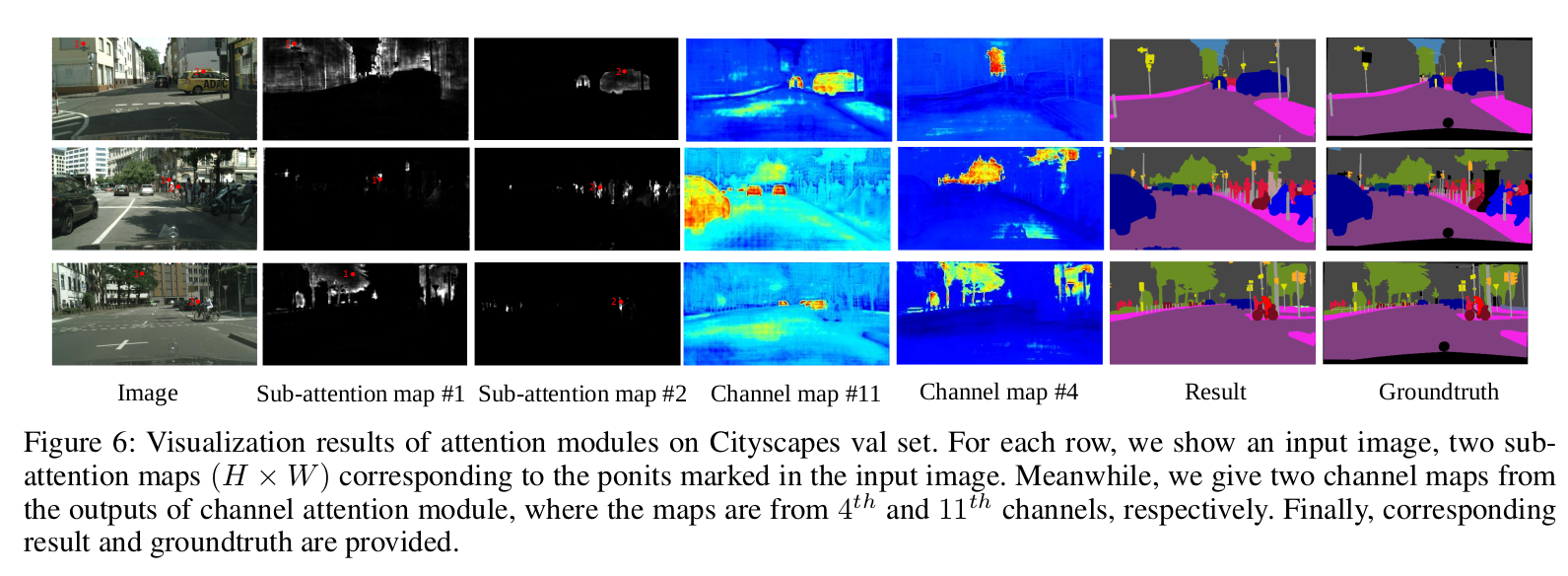
The convolution operations have a local receptive field, the features corresponding to the pixels with the same label do have some differences. These differences affect the recognition accuracy of traditional FCN’s. To address this issue, the DANet capture global dependencies by building associations among features with the attention mechanism. This method could adaptively aggregate long-range contextual information, thus improving feature representation for scene segmentation.
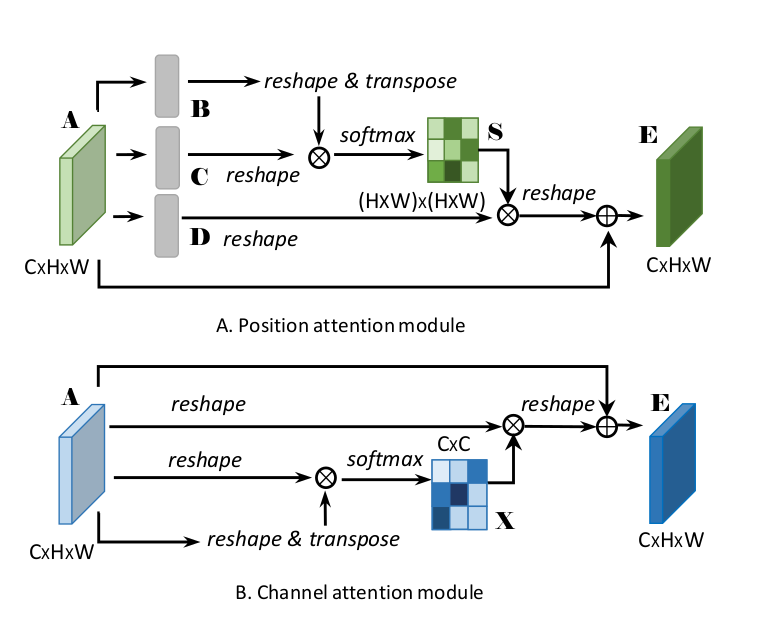
Position Attention Module
Context relationship is essential for scene understanding, which aims at capturing global dependencies regardless of locations. The position attention module encodes a broader range of contextual information into local features, thus enhancing their representative capacity.
Channel Attention Module
Each channel map of high-level features can be associated with a class-specific response. The interdependencies between channel maps could emphasize interdependent feature maps and improve the feature representation of specific semantics. Therefore, this channel attention module is built explicitly for model interdependencies between channels.
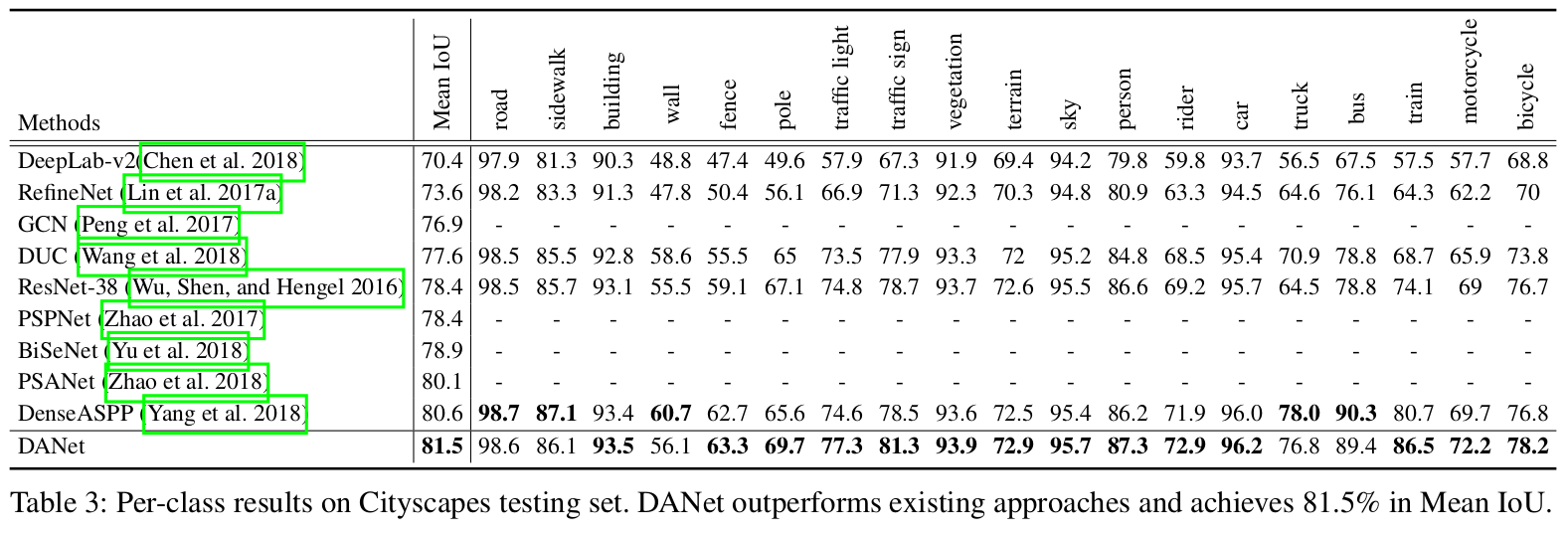
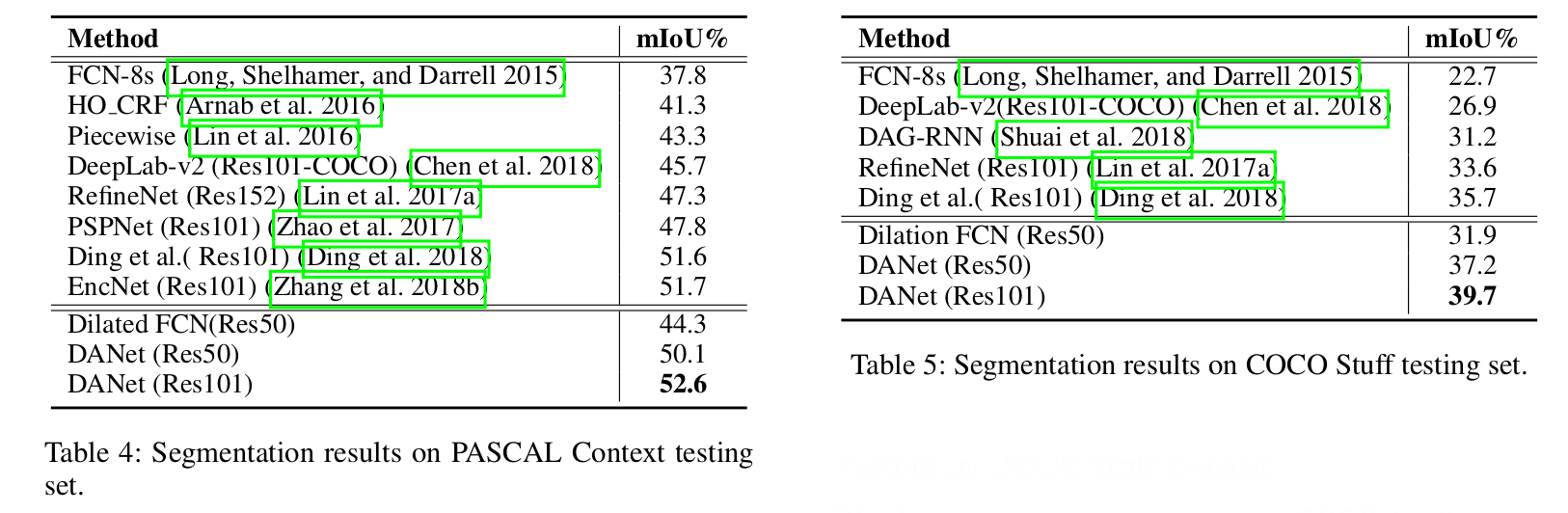
Results