Attentive Generative Adversarial Network for Raindrop Removal from A Single Image
Description
This paper aims at removing raindrops from color images. It does so with a GAN framework i.e.: with a generative network that generates an image void of raindrops and a discriminative network that tries to differentiate between fake and real images. C.f. Fig.2. Most of the contribution of the paper lies in the generative network.
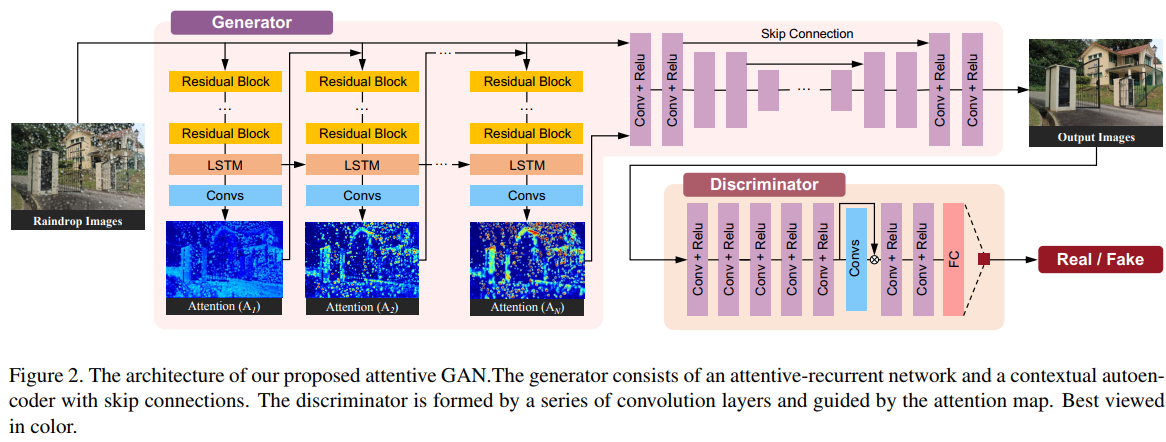
The generative network
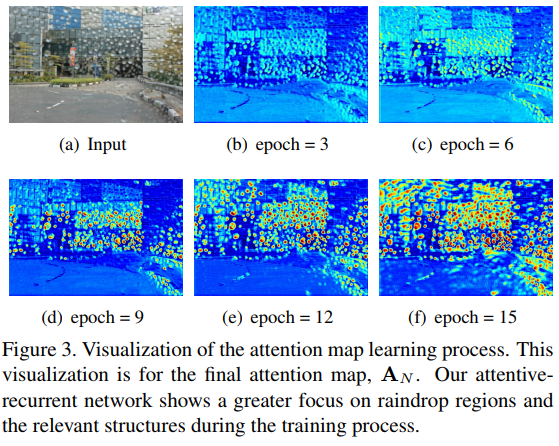
The first section of the generative network is a recurrent network (with LSTM) that aims at localizing raindrops. It does so by iteratively predicting attention maps (c.f. fig.3).
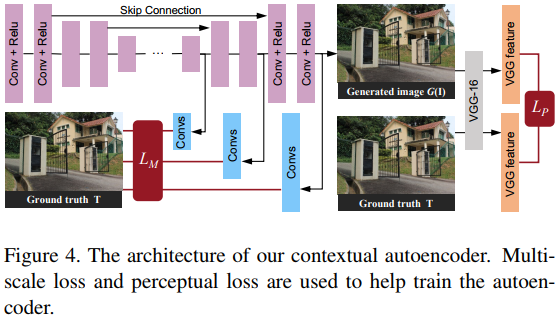
Once the attention map is been estimated, it is fed to an autoencoder together with the input image. The output of the decoder is the expected image. More details on the autoencoder is shown in Fig.4
The resulting loss contains 4 terms:
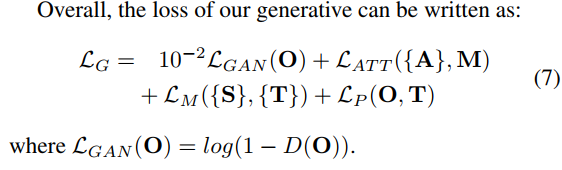
a GAN loss, an attention loss (to force the attention map A to look like the groundtruth mask of the drop M), a multiscale loss and a perceptual loss. The multiscale loss is the sum of the MSE between the groundtruth image T and the predicted image O at every scale of the network : \(L_M = \sum_s MSE(T_s-O_s)\). The perceptual loss is an L2 norm between the VGG code of the predicted image O and the groundtruth image T : \(L_p=\|VGG(O)-VGG(T)\|^2\).
Results
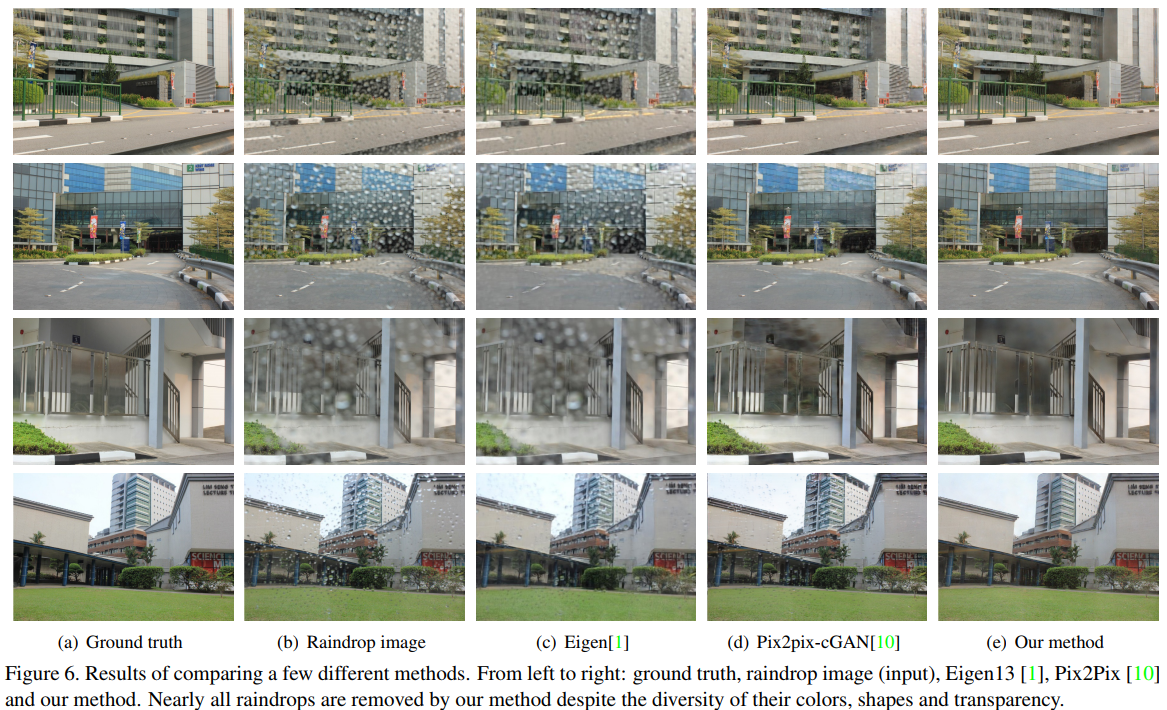
The method rocks!
