Training of Convolutional Networks on Multiple Heterogeneous Datasets for Street Scene Semantic Segmentation
Full implementation code for training, evaluation and inference, and the extra annotated datasets will be made publicly available here.
Idea
A convolutional network with hierarchical classifiers for per-pixel semantic segmentation, which is able to be trained on multiple, heterogeneous datasets and exploit their semantic hierarchy. The network is the first to be simultaneously trained on three different datasets: Cityscapes, GTSDB and Mapillary Vistas. The network is able to handle different class imbalances and different annotation types (per-pixel and bounding-box). Their implementation achieves inference rates of 17 fps at a resolution of 520x706 for 108 classes.
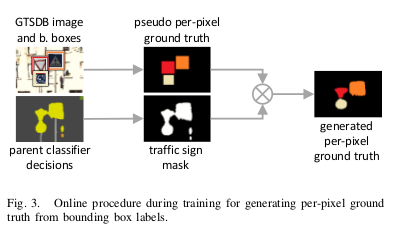
To include the GTSDB during training, they propose a new hierarchical loss.
\[L^{j}=-\dfrac{1}{|P^{j}_{1}|}\sum_{p\;\epsilon\; P^{j}_{1}}\log{\sigma^{j,p}_{y^{j,p}}}-\dfrac{1}{|P^{j}_{2}|}\sum_{p\;\epsilon\; P^{j}_{2}}\log{\sigma^{j,p}_{y^{j,p}}}\]Where \(|\cdot|\) is the cardinality of the pixel’s set, and \(y^{j,p}\;\epsilon\; C^j\) selects the element of \(\sigma\) that corresponds to the ground truth class of pixel p for classifier j. Pixels \(P_1^j\) with per-pixel annotations are trained using the standard one-hot cross-entropy loss. Pixels \(P_1^j\) with non-per-pixel annotations are trained with generated per-pixel ground truth using a modified cross-entropy loss.
Initiative
To increase the number of recognizable classes they use existing auxiliary datasets only for new (sub)classes. In that case, all classes of GTSDB are subclasses of the traffic sign class in Cityscapes. The straightforward approach of combining classes from both datasets in a conventional flat classifier is infeasible since a traffic sign pixel cannot have different labels depending on the dataset it comes from.
To summarize, the contributions of this work to per-pixel semantic segmentation are:
- A methodology for combined training on datasets with disjoint, but semantically connected, label spaces.
- A modular architecture of hierarchical classifiers that can replace the classification stage in modern convolutional networks.
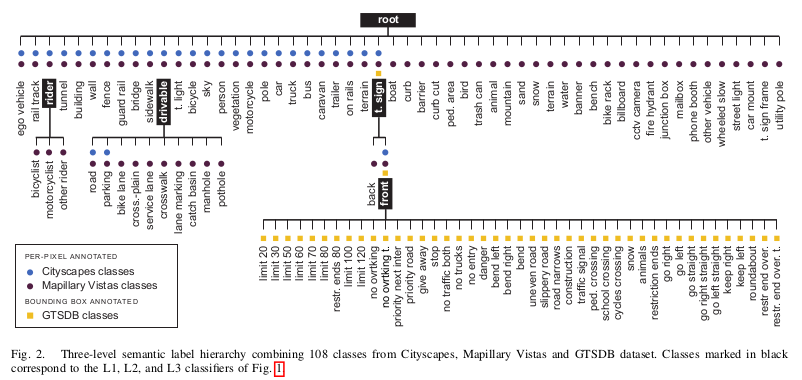
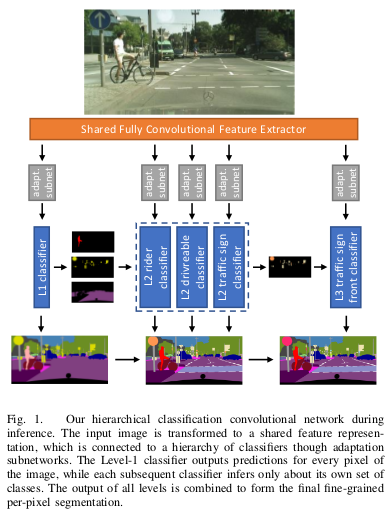
Semantic hierarchy of label spaces
Multiple dataset training requires a common label space for all selected datasets. They combine individual label spaces into the common space, containing labels from all datasets, by a hierarchical manner into a semantic tree of labels. This approach solves any conflict in the semantic definition of labels, by introducing the necessary parent or intermediate nodes and/or grouping of existing labels.
Each classifier (root, rider, drivable, t. sign, front) classifies the children labels of a node and the whole tree of classifiers are trained, in an end-to-end.
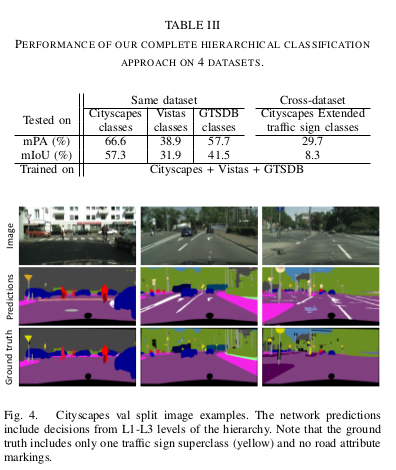
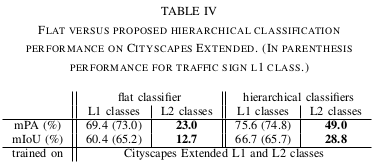
Results