Interactive Image Segmentation with Latent Diversity
Description
What is interactive segmentation?
It allows the user to segment the desired region in the image by successively placing positive (‘foreground’) and negative (‘background’) clicks. Every time a click is placed, the segmentation is updated. Once the segmentation matches the region intended by the user, the process concludes.
In this paper, they trained a model which couples two convolution network. This model takes an image and the clicks as input and produces the segmentation on click object.
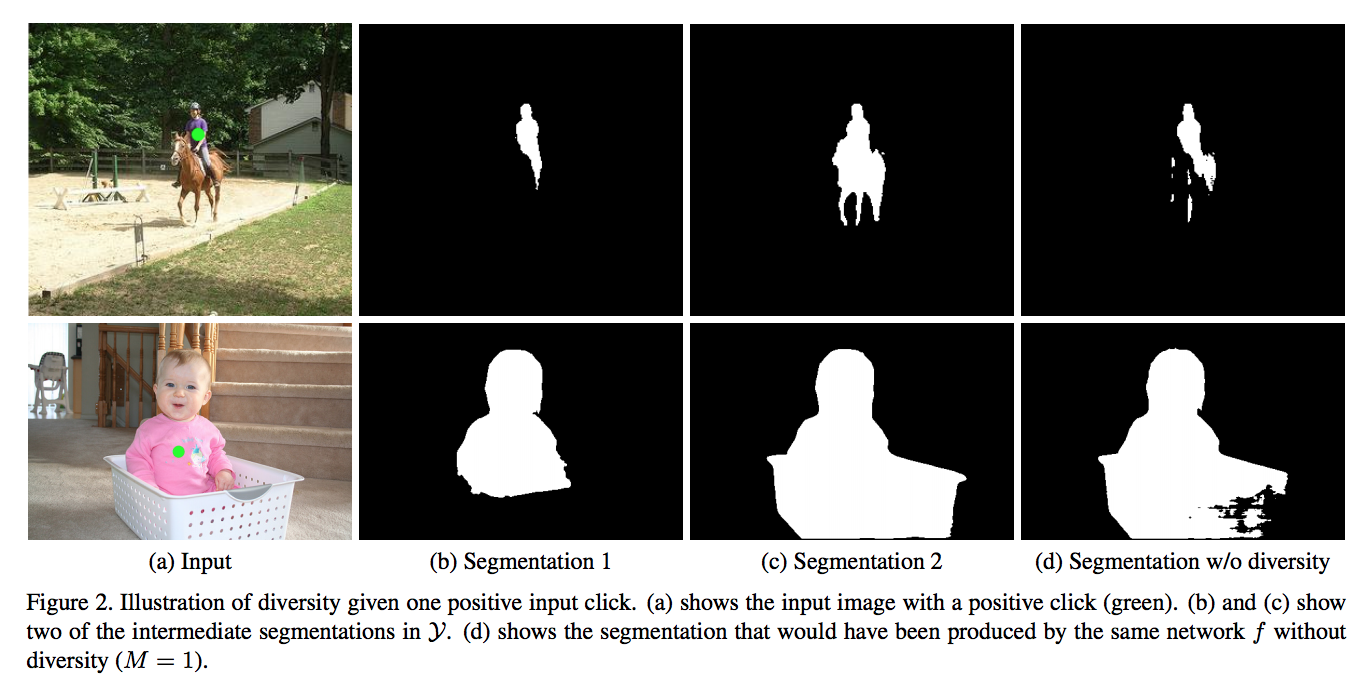
First, a network synthesizes M segmentations f(x) = y, which y is a collection of segmentation masks. Second, a network g selects one of the M solutions synthesized by f. This intermediate representation y allows the network f to produce multiple clean segmentations. Then, the network f produces plausible segments for another network(g) to select from. So, g takes a representation of the input and the synthesized segmentation masks, and produces a probability distribution over {1, . . . , M}.
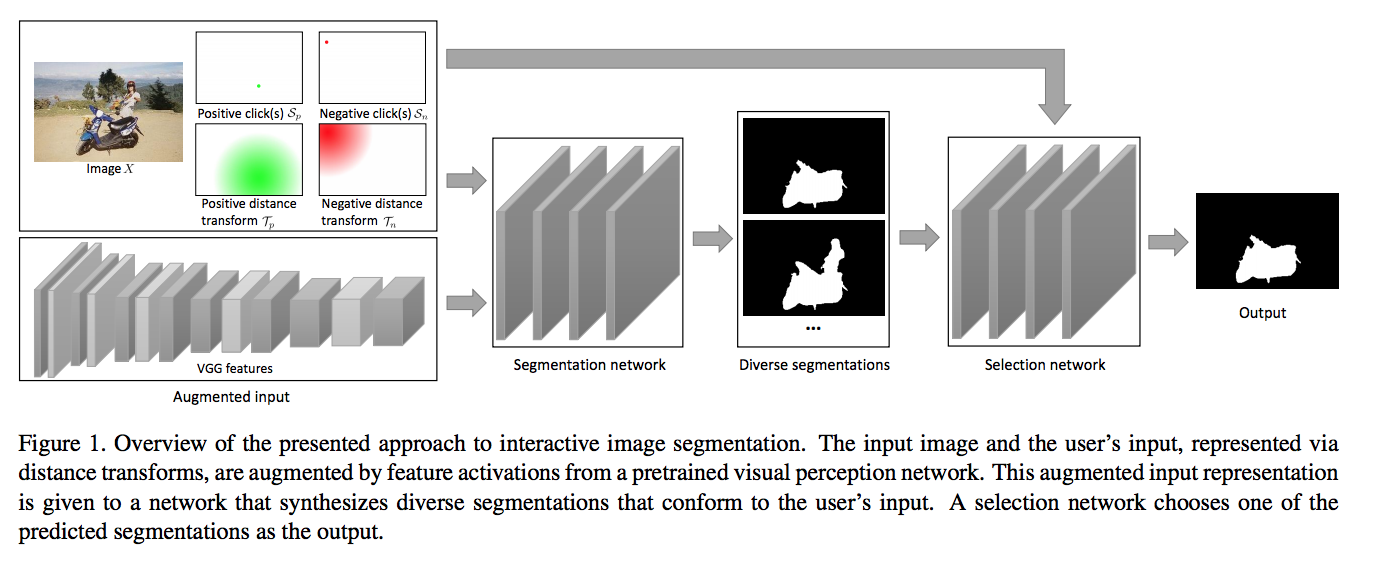
The input to the segmentation network f consists of the image X, clicks Sp(positive) and Sn(negative), distance transform where uses a Euclidean distance transformation and calculates the minimum Euclidean distance between a click point pixel and other pixels. In addition, they applied a VGG-19 network pre-trained on ImageNet dataset to the image x and extract the feature maps.
To produce a diversity segmentations, they applied Jaccard distance to measure the distance between the ground truth segmentation mask A(p) and predicted mask B(p)at pixel p. In addition, the input clicks are soft constraints where the Hadamard elementwise product is applied to Sp and predicted masks.
Finally, The selection network, takes an input and is trained
with the cross-entropy loss.
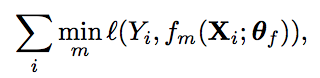
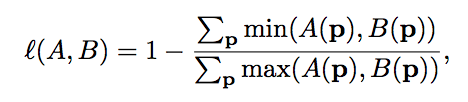
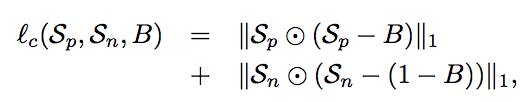
Experiments