Revisiting Dilated Convolution: A Simple Approach for Weakly- and Semi- Supervised Semantic Segmentation
The authors propose using dilated convolutions for weakly-supervised semantic segmentation. In particular, they designed their method for when we only have the image labels.
As we can see below, the dilated convolution allows to transfer informations to neighboring pixels.

The model is describe below, it takes the features maps from a classification network and then use several dilation schemes to extract features.
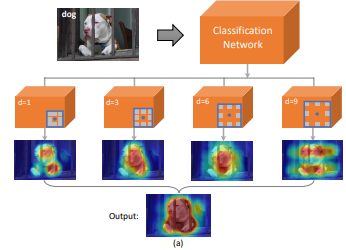
The final segmentation map is \(H = H_0 + \frac{1}{n_d} \sum_{i=0}^{n_d}H_i\) where \(H_0\) is the output without dilation and \(n_d\) is the number of dilation scheme.
To train the network, they compare \(H\) to the output of a saliency detector.
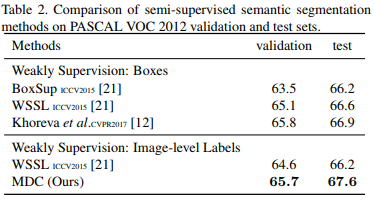
By adding a CRF at the end, they get SotA results on Pascal.
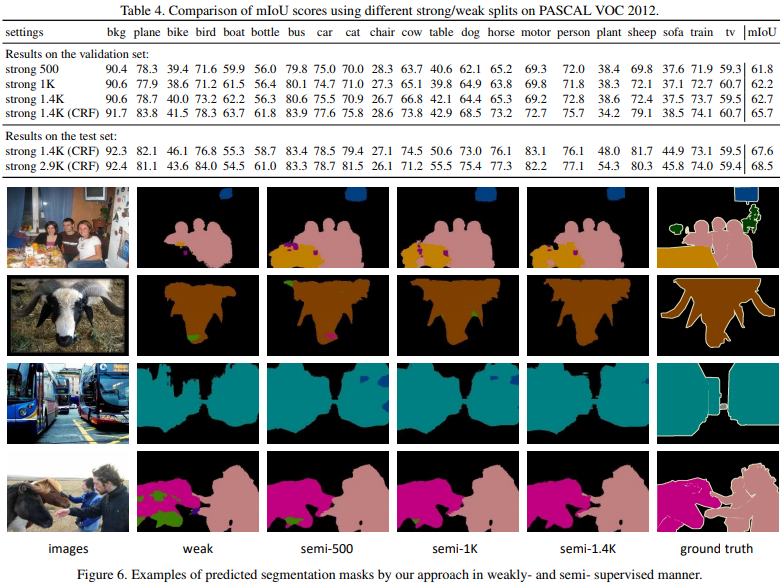
By training their network with 2.9k strong samples (ie. samples fully-annotated) they can get much better results.