Between-class Learning for Image Classification
Intro
In an other paper 1, they proposed a learning method named Between-Class learning (BC learning) for song recognition.They generated between-class examples by mixing two sounds belonging to different classes with a random ratio.They then input the mixed sound to the model and trained the model to output the mixing ratio of each class.
The advantages of BC learning are not limited only to the increase in variation of the training data. They argued that BC learning has the ability to impose constraints on the feature distributions, which cannot be achieved with standard learning, and thus the generalization ability is improved.
They achieved a performance that surpasses the human classification accuracy.
This paper tries to answer the question : does BC learning also applied to images?
The main idea
They argue that CNNs have an aspect of treating input data as waveforms. Thus, a mixture of two images can be seen as a mixture of two waveforms.
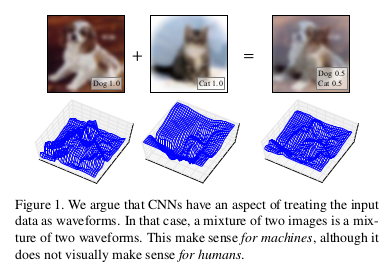
- Applied BC learning to images by mixing two images to train the model and output a mixing ratio.
- Argued of treating input data as waveforms and proposed a method to treats thus.
- Domonstrated the effectiveness of BC learning for images.
Mixing method
- Simple mixing: \(r x_1+(1-r)x_2\) where \(r = U(0, 1)\) and \(x_1, x_2\) the two images.
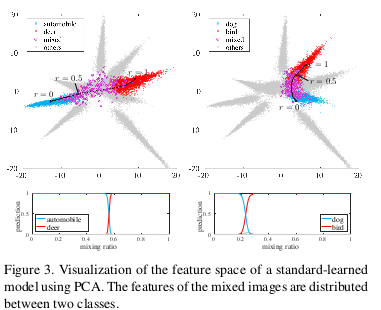
- BC+ Images as waveform data: image data as a 2-D waveform consisting of (R, G, B) vectors. Input data is normalized for each channel using the mean and standard deviation calculated from the whole training data.
\(\frac{p(x_1-\mu_1)+(1-p)(x_2-\mu_2)}{\sqrt{p^2 + (1-p)^2}}\) with \(p=\frac{1}{1+\frac{\sigma_1}{\sigma_2}\cdot \frac{1-r}{r}}\) \(\sigma_1,\sigma_2\) (the standard deviation per image)
Experiments
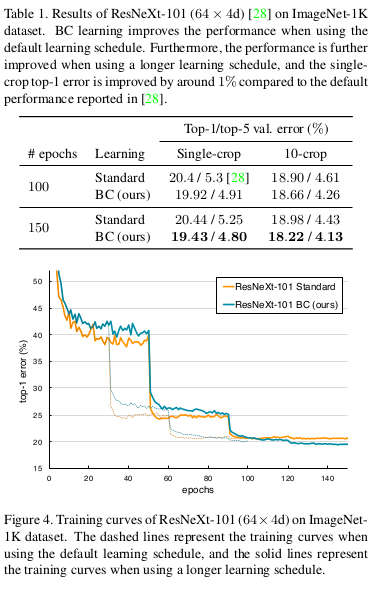
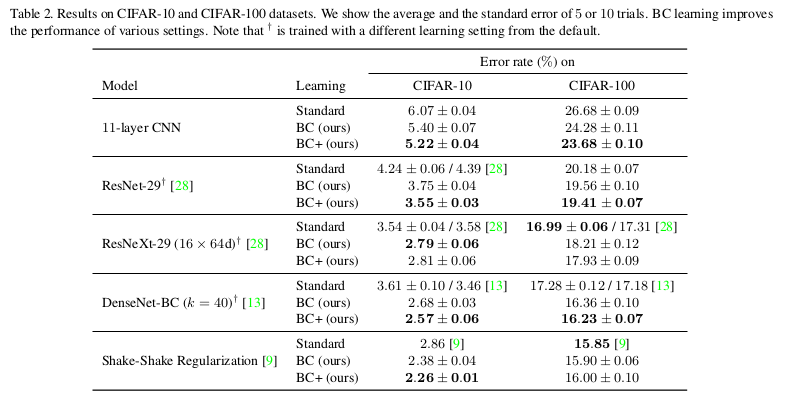
-
Y. Tokozume, Y. Ushiku, and T. Harada. Learning from between-class examples for deep sound recognition. In ICLR, 2018. https://openreview.net/ forum? id=B1Gi6LeRZ ↩