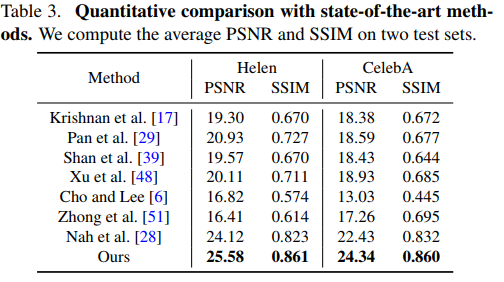
Deep Semantic Face Deblurring
This paper presents a simple, but effective idea. We can help the network to learn hard tasks by teaching it other simple tasks. Those intermediate outputs are considered priors to the hard task.
In this work, the authors propose an adversarial model which produces two outputs. It first does part segmentation and then, the segmentation is used as a prior to do deblurring.
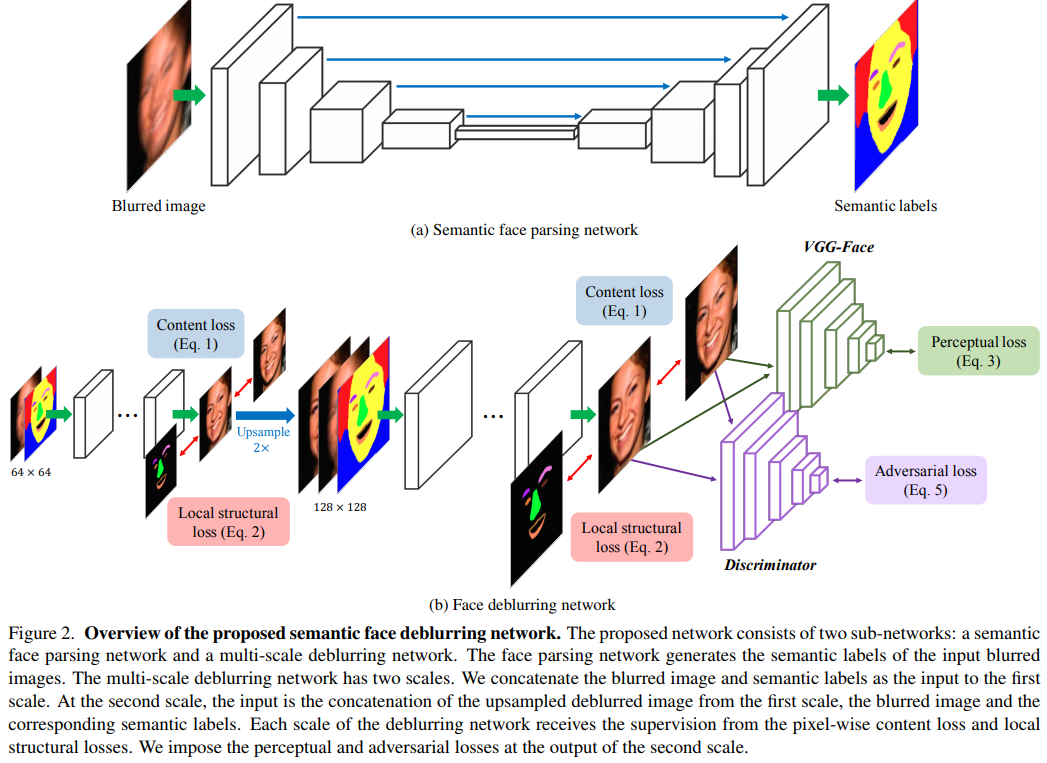
Losses
The network has four losses, the first two are the pixel-wise MAE and the adversarial loss.
To better segment small components such as lips or eyes, they introduce a structural loss.
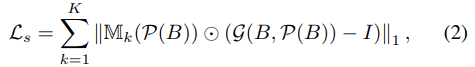
Where \(M_k\) is the mask associated with the class \(k\).
The last loss is a loss often used in style transfer, the perceptual loss. The idea behind this loss is that given an input and its transformed image, the same features should be extracted from a trained model for both images. In this case, they use VGG16 pretrained on VGG-Face.
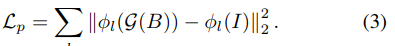
Where \(\phi_l(x)\) is the output at layer \(l\).
Training
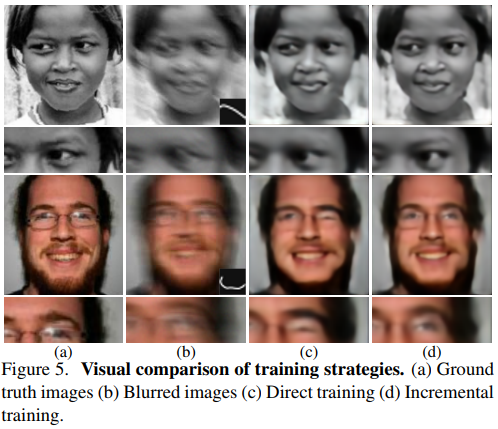
They use incremental training, meaning that they slowly increase the blurring kernel size. This helps the network avoid local minima.
Results
They show great results on both CelebA and the Helen dataset.