Generative Adversarial Networks and Probabilistic Graph Models for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Description
This paper opens the door to the use of GANs for hyperspectral Images classification. They show the efficiencyy of different GANs combined with conditional random fields. The reason for using GANs is to leverage the full potential of large amount of unlabled data.
Datasets
Methodology
Inspired by semi-supervised GAN, they proposed a spectral-spatial convolutional layer to construct both discriminators and generators with input an hyperspectral cube. In addition to that, they use a CRF to refine the posterior probability. The loss is not suitable for GANs so they include labeling information to generalize the GANs to semi-supervised tasks.
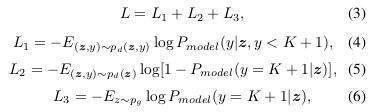
- L1: supervised loss
- L2: unsupervised loss for cheating discriminator
- l3: unsupervised loss for generator
They applied a fully -connected CRF that takes all pixels in a HSI and its corresponding predicted labels in classification map as and links them together to build a graph.
Experiments Results
- Spectral-Spatial GAN (SS)
- Autoencoder (AE)
- CNN + PCA (CNN-PCA)
- traditional CNN, spatial only network (SPA)
- Spectral only network (SPC)
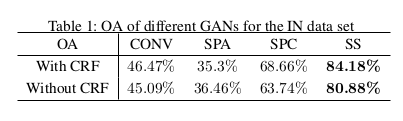
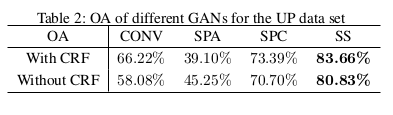
Conclusions
Promising results and opens a window for semi-supervised learning of hysperspectral image classification.
- That article can be joined to another article “Non-local tensor completion for multitemporal remotely sensed images inpainting”3 (non deep-learning article) in which they implemented a new method to reshape multitemporal spectral images with better results.