Data Distillation: Towards Omni-Supervised Learning
Description
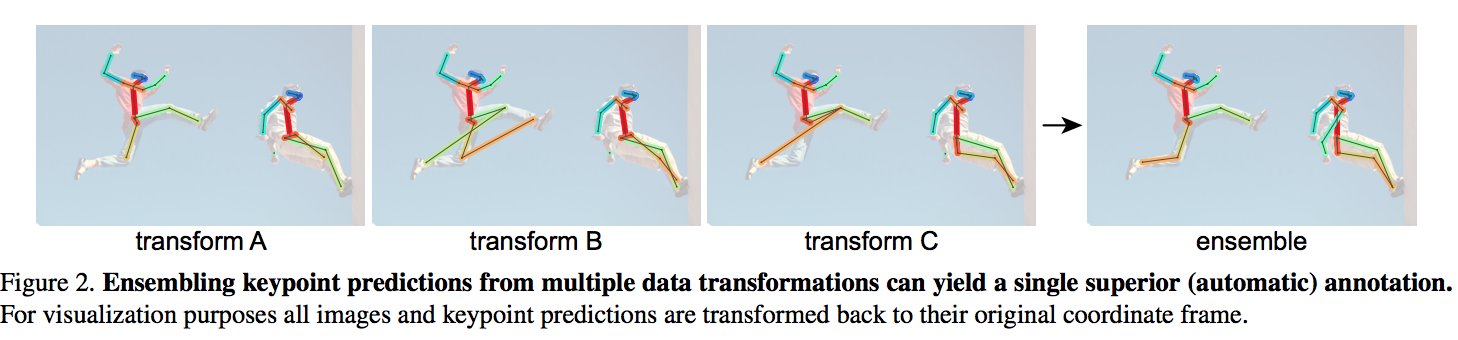
The goal of this work is to predict on unlabeled data and using them to update the model as self-training without the requirement of training a large set of models. The authors proposed a method by ensembling the predictions from multiple transformations of unlabeled data, using a single model, to automatically generate new training annotation.
There is a single model which run on different transformations (flipping and scaling) of an unlabeled image and then ensemble the result. In comparison with distilling knowledge, which predictions of multiple models are considered, there is a single model runs on multiple transformed unlabeled images.
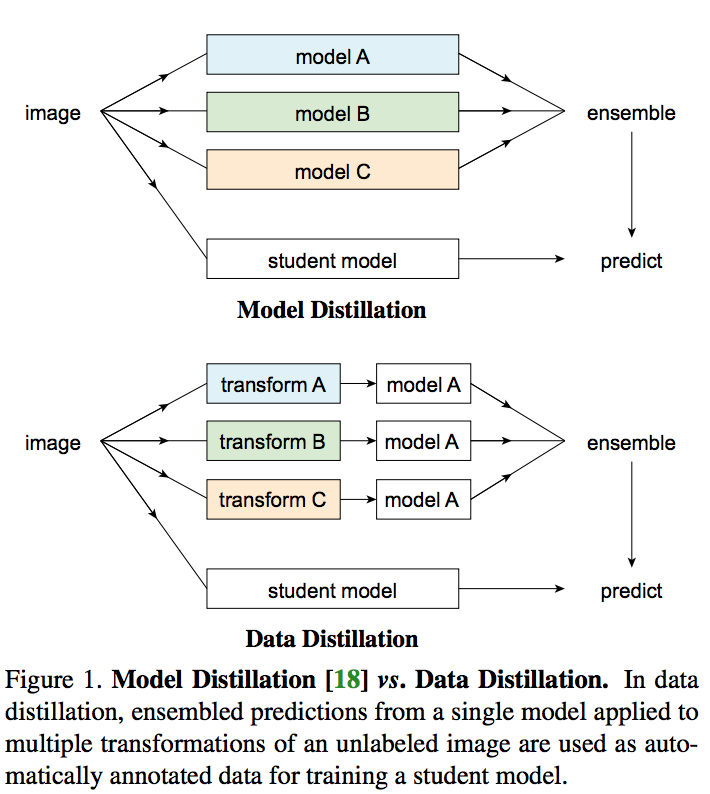
There is four steps for data distillation:
- training a model on manually labeled data.
- applying the trained model to multiple transformations of unlabeled data.
- converting the predictions on the unlabeled data into labeles by ensembling the predictions.
- retraining the model on the union of the manually and automatically labeled data.
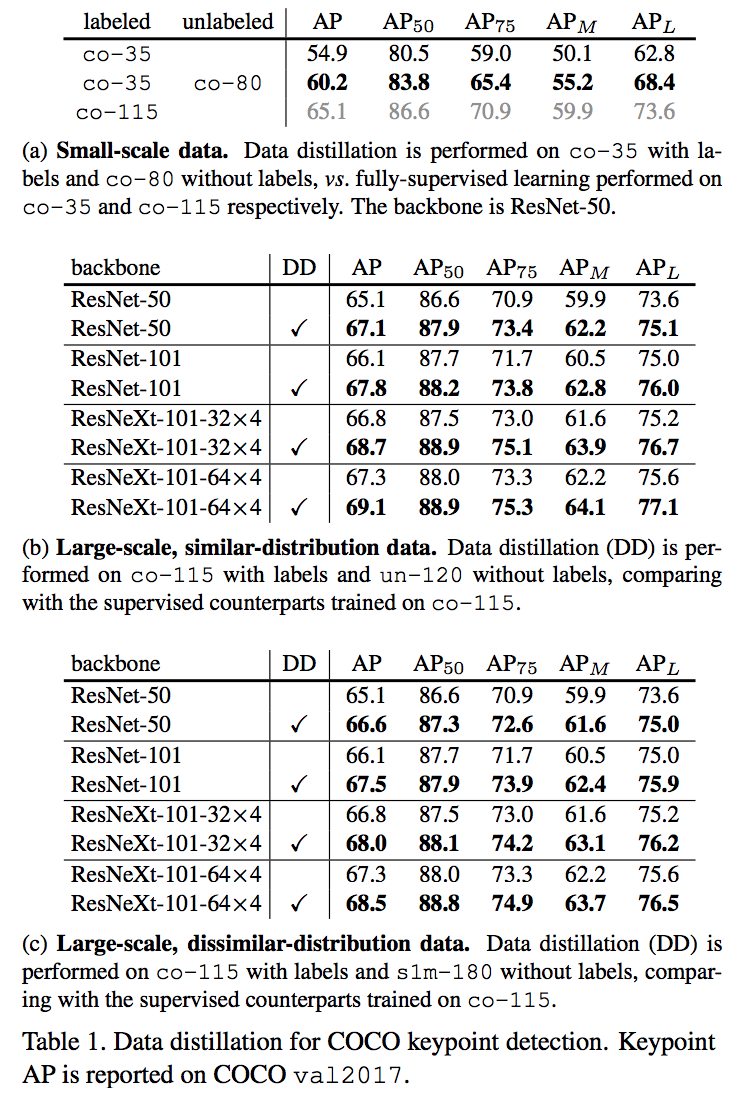
They trained a Mask R-CNN model to test data distillation on COCO dataset and Sport-1M.
There is tree type of scales:
- Small-scale: co-35(35k training images) as labeled and co-80 as unlabeled.
- Large scale with similar distribution: co-115 as labeled and un-120 as unlabeled.
- Large scale with dissimilar distribution: co-115 as the labeled and s1m-180 as unlabeled.
Results: