Unsupervised Learning of Depth and Ego-Motion from Video
Prerequisite
Novel view synthesis image: given one input view of a scene, synthesize a new view image of the scene seen from a different camera pose. If we have rotation, translation and intrinsic camera matrix (R,T,K) or depth and translation matrix (D,T), would be enough to generate new view image. If xis a cordinate of pixel in image, the following equation gives 3d cordinate in world.
\(x_{s} = K_{1} R_{1} T_{1} P_{w}\)
\(x_{t} = \acute{ K_{1}} \acute{R_{2}} \acute{T_{2}} P_{w}\)
\(x_{s} =K_{1} R_{1} T_{1} \acute{T_{2}}^{-1} \acute{R_{2}}^{-1} \acute{K_{1}}^{-1} x_{t}\)
Forward/Backward Warping : There are two ways to wrap an image. The first method is forward warping. In this method, every point in the original image is transformed and sent to its new location. However, this mode of warping can result in holes and splattering. The better approach is to perform inverse warping. This algorithm goes through every pixel in the new, transformed image, undoes the transformation, and figures out which original pixel to grab. If the original pixel happens to fall between two pixels, simply interpolate the source image.

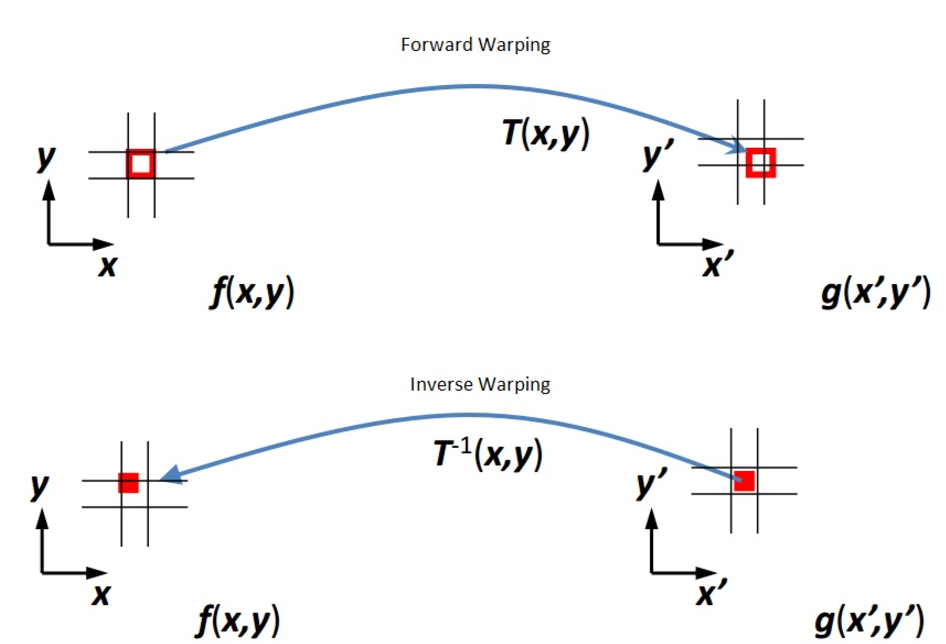
Note: Some factors corrupt the process such as: The scene is dynamic or there is occlusion between target and source images or surface is Lambertian.
Summary
The authors present an unsupervised and end to end method for novel view synthesis image by CNN and also it does not need the pose information, that it would be a part of learning framework. The proposed network contains two parts: depth prediction network and pose network. The depth network input is just target image and its output is depth prediction, also the pose network input is source images and target images and depth predictions as shown below.
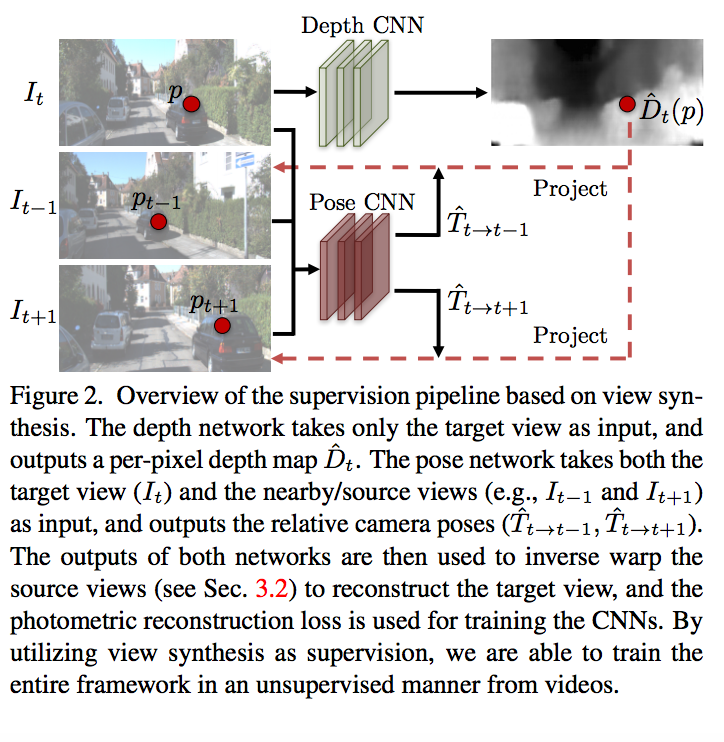
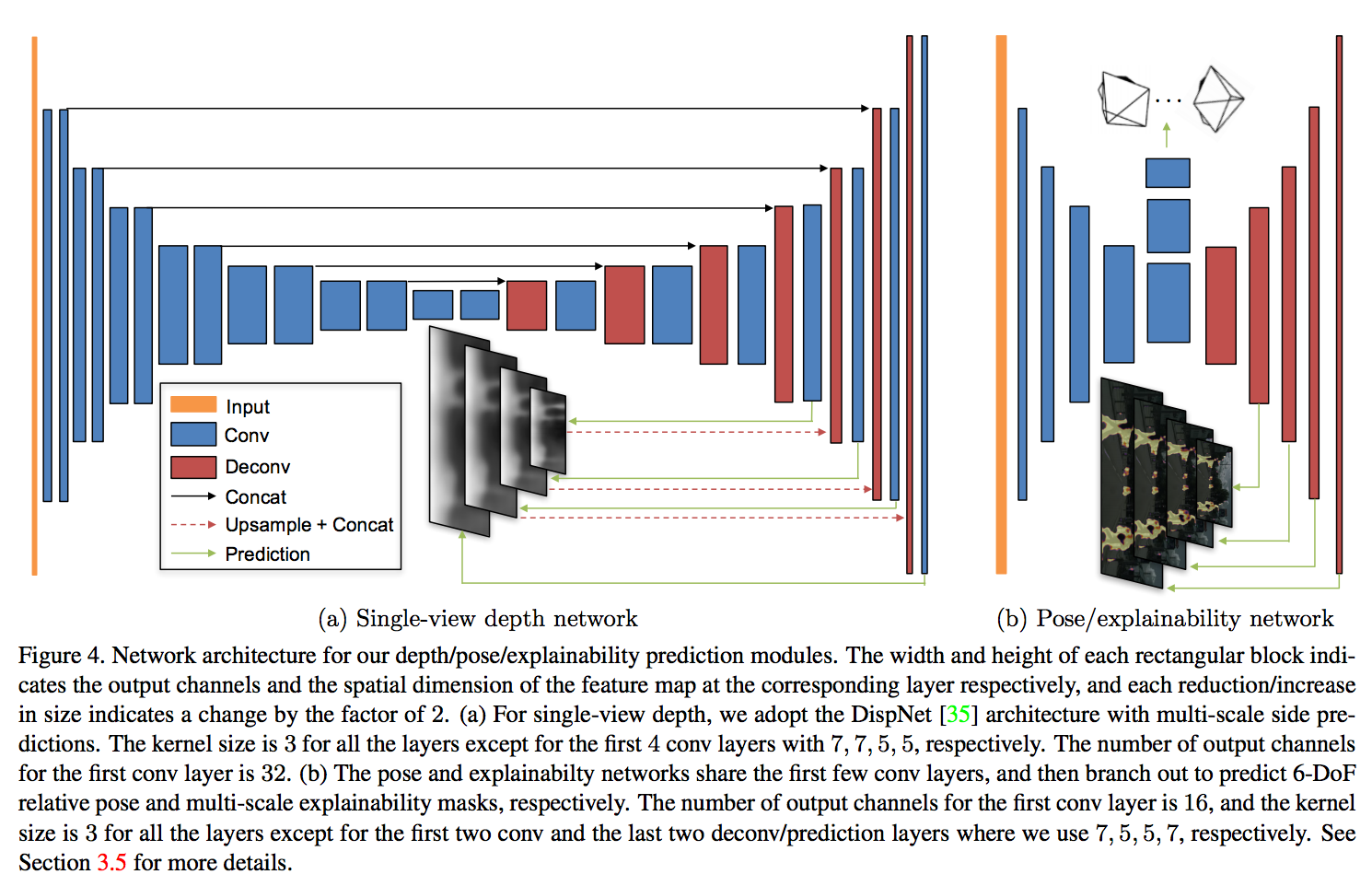
Depth prediction network is based on DispNet that is mainly an encoder-decoder with skip connections and multi-scale side prediction. The Multi-scale helps dealing with low-texture regions, so smoothness and multi-scale reduce this problem. The author improves the robustness into the factors (mention in the note), by adding a explainability mask network to indicate for each pixel in the source image, network successfully can find the corresponding pixel in the target image. The pose and explainability mask network share five first convolution layers then branch out to pose output and explainability mask, that followed by five deconvolution layer with multi scale predection as shown below.
The view synthesis objective can be formulate as:
\[l_{us} = \sum_{s}\sum_{p}| I_{t}(p) -\bar{I_{s}}(p)|\]But the explainability mask accounts for a per pixel parameter \(\bar{E_{s}}\) to encourage minimize the objective, but allowed a certain amount of discounting the factors not considered by the model.
\[l_{us} = \sum_{s}\sum_{p}\bar{E_{s}}| I_{t}(p) - \bar{I_{s}}(p)|\]Beacuse the network is unsupervised, then it is always predecting \(\bar{E_{s}}\) to be zero.Thus, they added a regularization term to the loss. Then final objective is:
\[l_{final} = \sum_{L}l_{us}^l + \lambda_{s} L_{smooth}^l + \lambda_{e} \sum_{s}l_{reg} \bar{E_{s}^l}\]Where \(l\) indexes over different image scale, \(s\) indexes over source images and \(\lambda_{s}\)and \(\lambda_{e}\) are weighting for depth smoothness loss and explainability regularization.
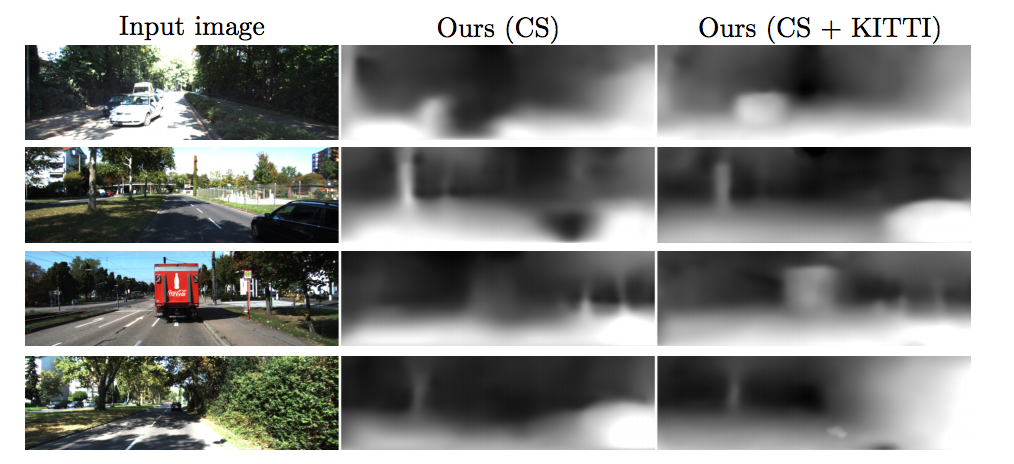
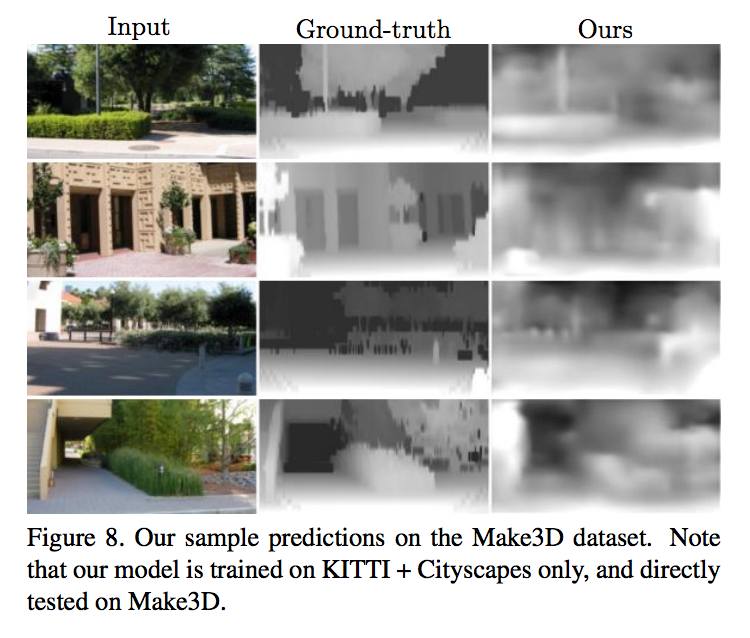
Depth Result


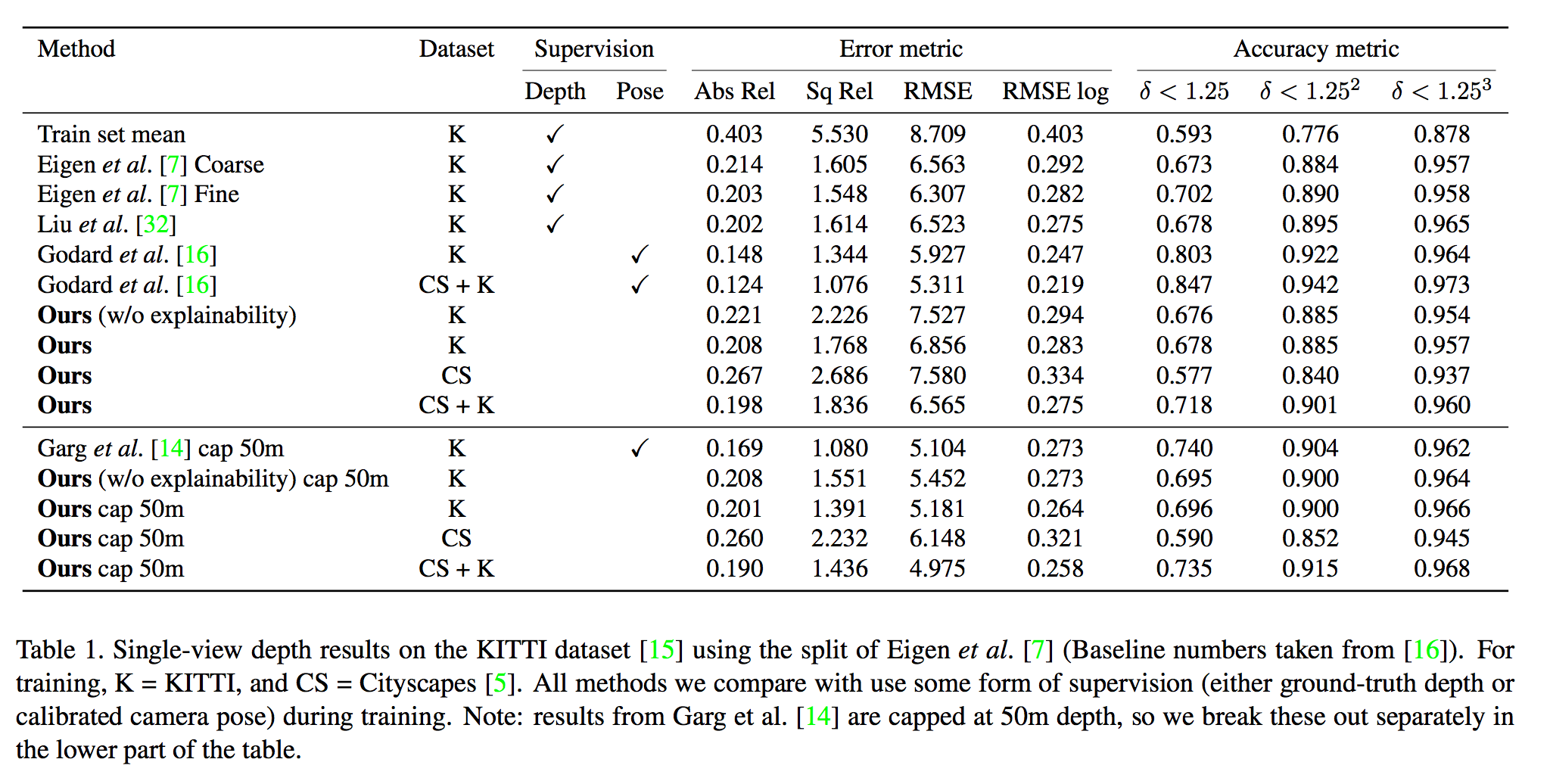
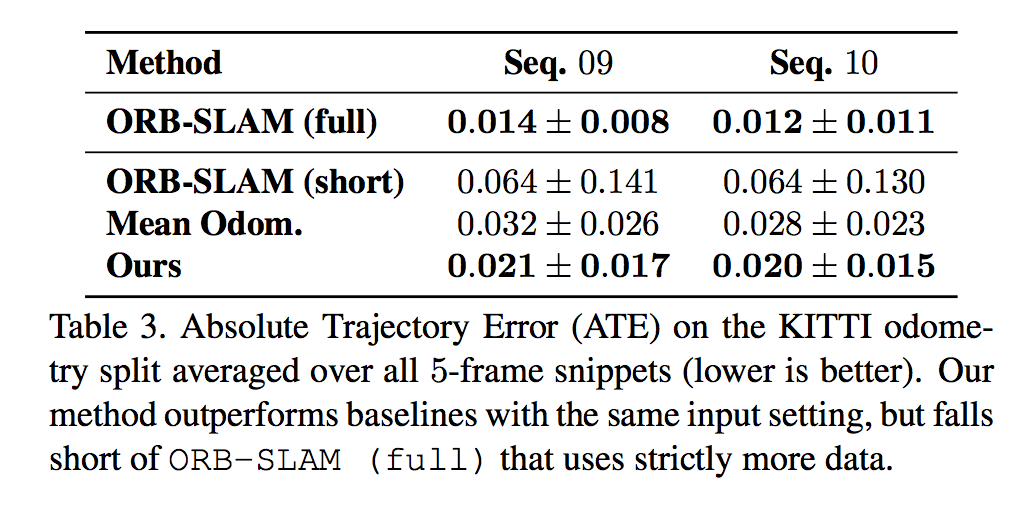
Pose Estimation
Explainability mask Result

Code
The code is available at https://github.com/tinghuiz/SfMLearner.