Pixelwise Instance Segmentation with a Dynamically Instantiated Network
In this paper, the authors use localization and semantic segmentation to perform instance segmentation.
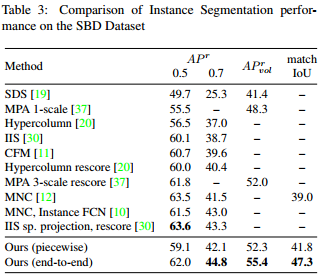
Their end-to-end network, which outputs a variable number of instances per input image, begins with an initial semantic segmentation module. The following dynamic part of the network uses information from an object detector and a Conditional Random Field (CRF) model to distinguish different instances.
An important note is that you need to guess \(D\) the number of instances in the image.
They did some work on the loss function to avoid ordering error. In other models, labeling the first person \(2\) and the first one \(1\) would be an error. (Sec 3.4)
CRF
The CRF takes three terms. First, the box term encourages a pixel to be assigned to a box if it’s inside of it. Second, the global term which assigns a segmented pixel without a box to an instance. Finally, the shape term which uses prior shapes to assign pixels. This term helps with merged objects.
To train the network, they train the segmentation part first and then finetune with the instance segmentation network. The RPN is not trained.
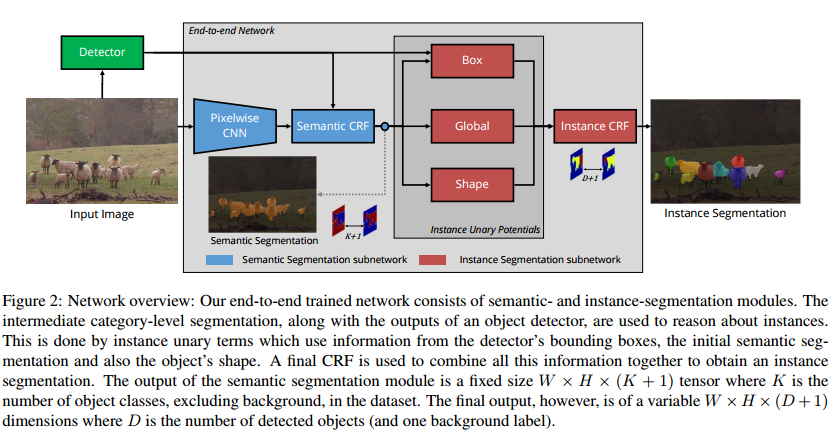
The proposed method is state of the art for a high IoU threshold (> 0.7) on PASCAL VOC and SBD. In the following figure, the piecewise version is that they froze the segmentation part to only fine-tune the instance segmentation subnetwork.