Instance-Level Salient Object Segmentation
Instead of only doing salient object detection, the method proposed in this paper also segment different salient objects into different instances.
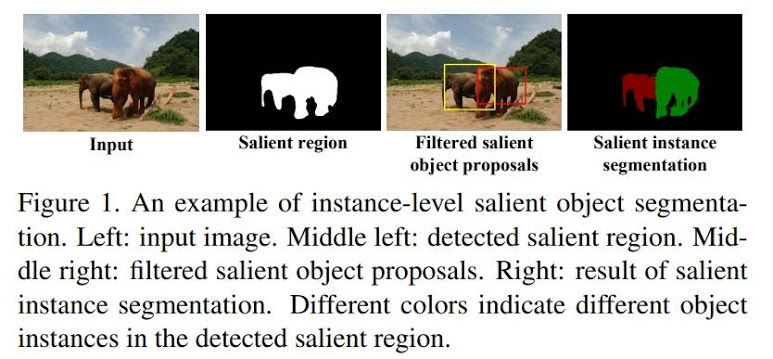
Contributions
- A new dataset (1000 images of instance-level salient objects).
- A multi-scale segmentation network.
Framework
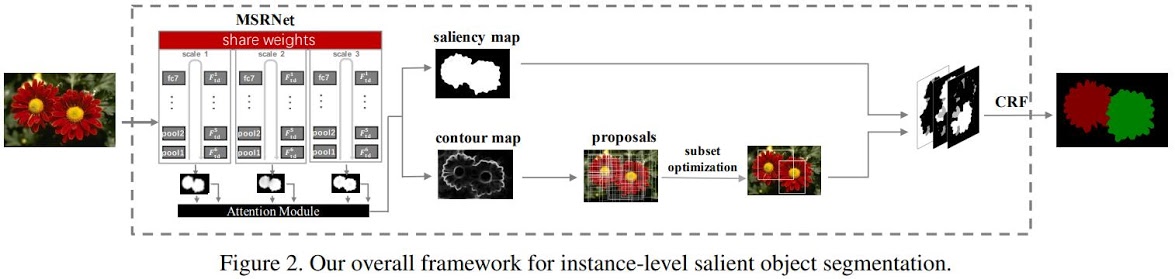
- A multi-scale segmentation network is used to compute the saliency map and contour map.
- The multiscale combinatorial grouping (MCG) algorithm [1] was used to generate object proposals, and the subset optimization method [2] selected the final salient proposals.
- A fully connected CRF step [3] was adopted to get the final instance segmentation.
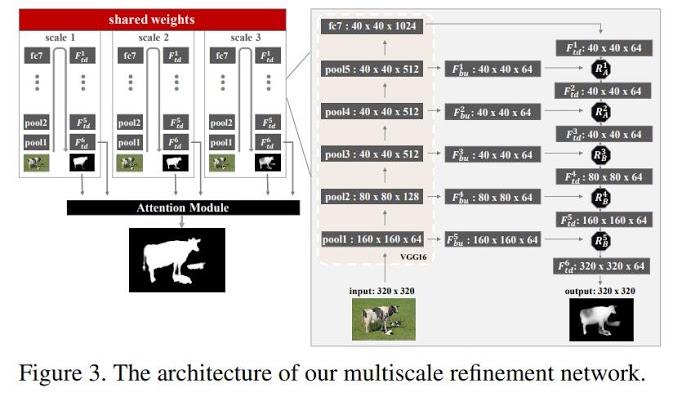
1. Multiscale segmentation network
- A U-Net like network architecture fusing segmentation result from multiple scales.
2. Proposal step
- 800 salient object proposals for any given image based on the contour map.
- Discard those proposals with fewer than 80% salient pixels
- The subset optimization is used produce a compact set of object proposals. (The final number of instances)
3. CRF step
- Suppose the number of salient instances is K, and the background is treated as K+1 class.
- Define a probability map with K+1 channels
- If a salient pixel is covered by a single detected salient instance, the probability of associated instance channel is 1.
- If a salient pixel is not covered by any detected salient instance, then set the probability of each instance channel to 1/K .
- If a salient pixel is covered by m overlapping salient instances, the probability of associated m channels is 1/m.
- If a background pixel is covered by m overlapping salient instances, the probability of associated m channels is 1/(m+1), and the background channel is also 1/(m+1).
- If a background pixel is not cover by any instance, then the background channel is 1.
- A fully connected CRF is used for the final segmentation.
Experiment Result
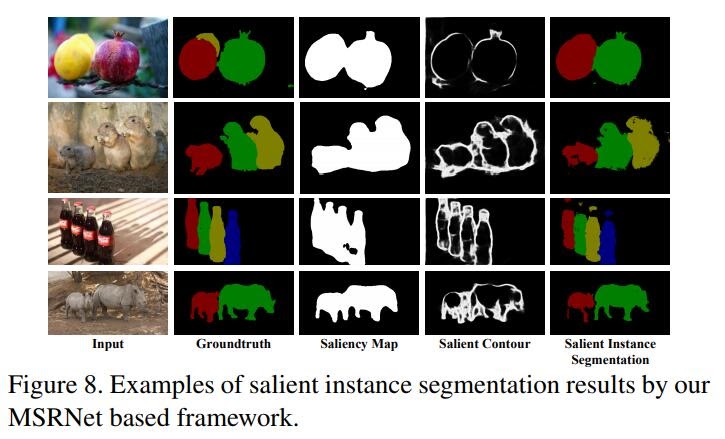
The Multiscale segmentation network for saliency detection
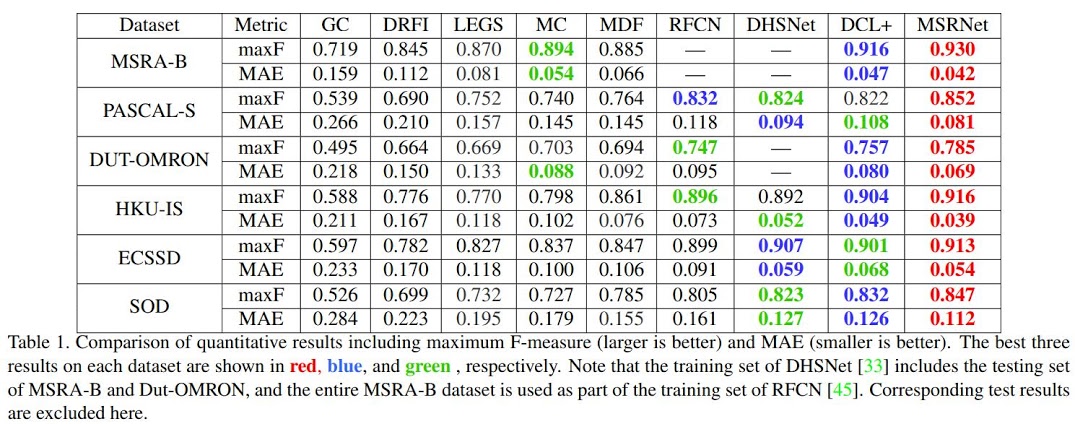
Instance-Level segmenation
