V-Net : Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation
A new MRI segmentation method of the prostate based on a 3D CNN similar to the U-Net. The results are reported on the prostate challenge PROMISE2012.
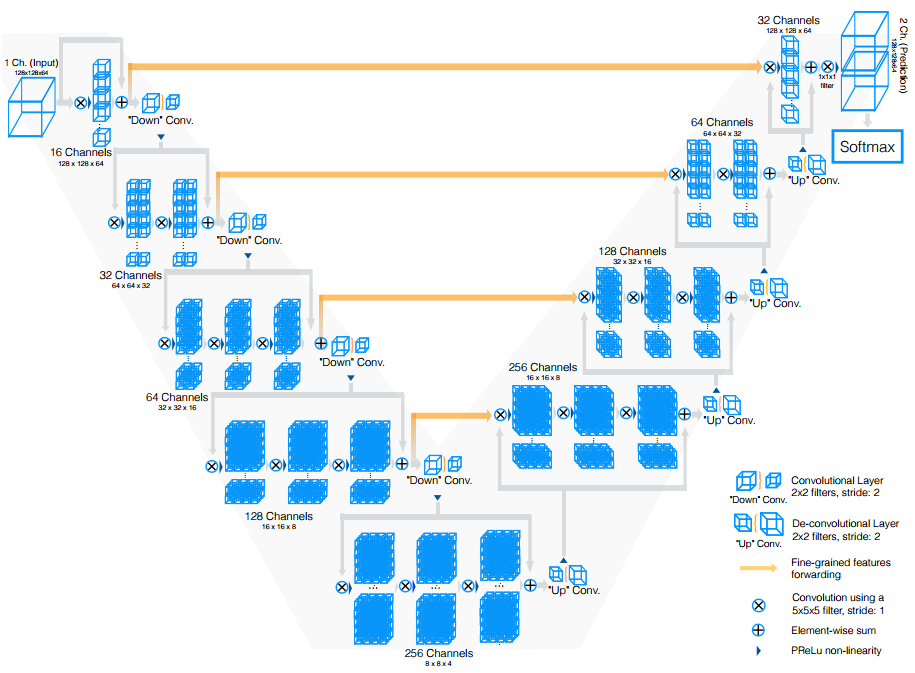
Architecture
To achieve this task they use 3D convolutions to ensure the correlation between adjacent slices. The architecture of the network is similar to the U-Net. They use only a kernel size of \(3 \times 3 \times 3\).
Input
The training is done by extracting patches from the training set, this as two purpose, the first is some kind of easy data augmentation and the second it’s easier to train because you can balance the data in the image at least same proportion of prostate & non prostate pixels.
Data augmentation
Due to a limited number of annotated volumes for training they augment the data by applying random non-linear transformation (dense deformation field and B-Spline interpolation) and histogram matching.
Loss
They introduce a Dice loss layer which is computing the dice between the binary target and the probability output.
\[D = \frac{2 \sum_i^N p_ig_i}{\sum_i^N p_i^2 + \sum_i^N g_i^2}\]Where \(p_i \in P\) is the predicted binary segmentation and \(g_i \in G\) is the truth binary volume.
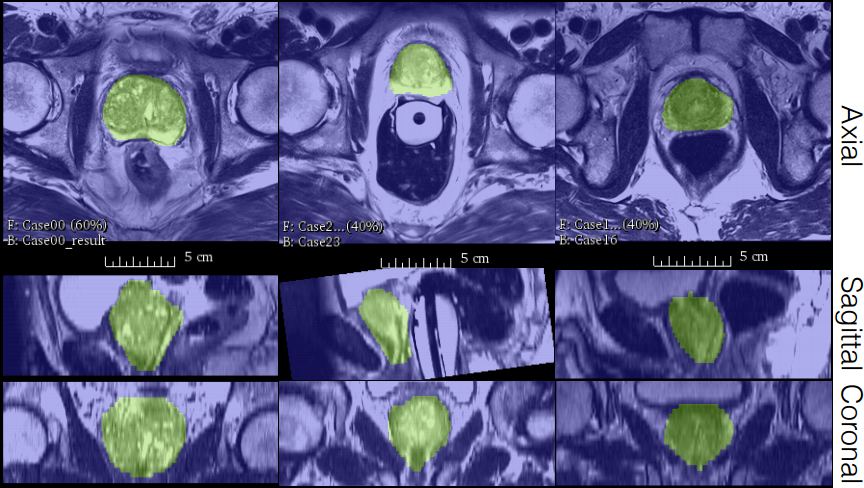
Results
The results of this method are pretty accurate.
Take home message
- This method introduce a new loss layer (Dice loss) for two class segmentation
- They use 3D convolution instead of 2D, like in U-Net.